| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
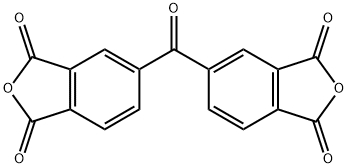
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride | [CAS]
2421-28-5 | [Synonyms]
BTDA
NOTAVAILABLE
LABOTEST-BB LT02097910
4,4'-Diphthalic anhydride ketone
4,4'-CARBONYLDIPHTHALIC ANHYDRIDE
Phthalic anhydride, 4,4'-carbonyldi-
4,4'-Carbonylbis[phthalic anhydride]
5,5’-carbonylbis-3-isobenzofurandione
Benzophenonetetracarboxylic anhydride
BTDA~4,4-Carbonyldiphthalic anhydride
5,5-Carbonylbis(1,3-isobenzofurandione)
3-Isobenzofurandione,5,5’-carbonylbis-1
3,3',4,4'-BENZOPHENONETETRACARBOXYLIC DI
BENZOPHENONE-TETRACARBOXYLIC-DIANHYDRIDE
5,5'-Carbonylbis(isobenzofuran-1,3-dione)
1,3-Isobenzofurandione, 5,5'-carbonylbis-
Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid anhydride
BENZOPHENONETETRACARBOXYLIC ACID DIANHYDRIDE
3,3',4,4'-Tetracarboxybenzophenone dianhydride
3,3',4,4'- twophenyl ketonefourtwo acidanhydride
3,3',4,4'-BENZOPHENONETETRACARBOXYLIC DIANHYDRIDE
BENZOPHENONE-3,3',4,4'-TETRACARBOXYLIC DIANHYDRIDE
3,3’,4,4’-benzophenonetetracarboxylicaciddianhydride
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride,96%
Benzophenone-3,3',4,4'-tetracarboxylic dianhydride 96%
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride ,99%
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid dianhydride
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, 98+%
3,3'',4,4''-BENZOPHENONETETRACARBOXYLIC DIANHYDRIDE 98%
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, 97+%
3,3'4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA)
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride ,99.5%
5-(1,3-Dioxo2-benzofuran-5-carbonyl)-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione
BENZOPHENONE-3,3'',4,4''-TETRACARBOXYLIC DIANHYDRIDE (BTDA)
3,3',4,4'-BENZOPHENONETETRACARBOXYLIC DI ANHYDRIDE, SUBLIMED, 98%
4,4'-Carbonylbis(benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid)1,2:1',2'-dianhydride
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation)
benzophenone-3,3',4,4'-tetracarboxylic dianhydride 4,4'-carbonyldi(phthalic anhydride) | [EINECS(EC#)]
219-348-1 | [Molecular Formula]
C17H6O7 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00005923 | [MOL File]
2421-28-5.mol | [Molecular Weight]
322.23 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white crystall powder | [Melting point ]
218-222 °C(lit.)
| [Boiling point ]
320°C 5mm | [density ]
1,57 g/cm3 | [vapor density ]
1.4 (vs air)
| [vapor pressure ]
<0.1 mm Hg ( 0 °C)
| [refractive index ]
1.6380 (estimate) | [Fp ]
324 °C
| [storage temp. ]
Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature | [solubility ]
DMF: 0.1 g/mL, clear
| [form ]
Needles or Crystalline Powder | [color ]
Off-white to brown | [explosive limit]
16% | [Water Solubility ]
REACTS | [Sensitive ]
Moisture Sensitive | [λmax]
580nm(CH3CN)(lit.) | [Sublimation ]
220-230 ºC | [BRN ]
761777 | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic | [InChIKey]
VQVIHDPBMFABCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
3.3 at 25℃ | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Bis-(3-phthalyl anhydride) ketone(2421-28-5) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
1,3-Isobenzofurandione, 5,5'-carbonylbis-(2421-28-5) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
Benzophenone-3,3',4, 4'-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA) is used as intermediate and in polycondensation (fiber and powder production) to manufacture plastic products or fine chemicals in the industrial sector. Consumer risk is very unlikely as BTDA is manufactured and handled under closed conditions in industrial settings only. The environmental effects, ecotoxicology and toxicology information available for BTDA is provided based on studies and/or a reliable evaluation of its hazardous properties. | [Uses]
BTDA is used as intermediate in the manufacture of plastic products or fine chemicals in the industrial sector. | [Physical properties]
BTDA is a tan-colored crystalline powder. The substance has a melting point of 218.67 °C and shows decomposition at 360 °C. The auto-ignition temperature is very high and no flammability is observed. The substance has a density of 1.5452 g/ml and a vapor pressure of 6.53E-011 Pa. The substance is slightly water soluble and has a log Pow of 3.3. | [Health Hazard]
BTDA has no acute toxicity by oral and inhalative route or by dermal exposure. The substance is irritating to eyes and the respiratory tract. BTDA is sensitizing to skin. BTDA is not mutagenic. | [Environmental effects]
Based on available data for the substance, BTDA is harmful to aquatic organisms with long lasting effects. The substance is not readily biodegradable and is not considered to have potential to bioaccumulate.BTDA is industrially used as monomer to manufacture the rmoplastics or another substance. The manufacture and handling is a closed process, thus only very limited exposure to the environment is expected. Any exposure from manufacture or use will generally be below the level of concern. |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white crystall powder | [Uses]
BTDA is important monomer of polyimide, and used for production of polyimide material. The material has high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, radiation resistance, insulation, shock resistance, excellent performance. Can be made into structure parts, laminates, films, adhesives, coatings, insulation materials and reinforcing material, etc., can be widely used in the field of aerospace, electrical / electronics, shipbuilding, automobile, precision machinery. | [Uses]
Used in the synthesis of polyimides. | [Application]
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA) is used for:
(1) Synthesis of polyimides
(2) Preparation of cellulose acetate (AC) hydrogels
(3) Curing epoxy powder coatings
(4) Preparation of nanocomposite films
(5) BTDA-formed polyimide/copolymer as dielectric layer for high-performance OFET memory devices | [General Description]
Benzophenone-3,3′,4,4′-tetracarboxylic acid is formed by hydrolysis, it can be converted to the dianhydride by treating with Ac2O (molar ratio 4 to 1 of acid).The dianhydride is used to synthesize polyimides, which are highly flexible in nature due to the presence of keto and carbonyl groups in the dianhydride molecule. The keto and carbonyl groups subsequently increase the spacing between the imide rings enhancing the solubility and processibility. | [Flammability and Explosibility]
Nonflammable | [Purification Methods]
The main impurity is the free acid formed by hydrolysis (check for OH bands in the IR). This can be converted to the dianhydride by treating with Ac2O (molar ratio of 4 to 1 of acid), heating at 110-120o for 1.5 to 2hours, cooling to 0—5o and collecting the dianhydride. This is then dissolved in hot dioxane or Me2CO, filtered and cooled to 10—15o. The moisture sensitive solid is collected and dried at 120—130o in vacuo. It has been sublimed at high vacuum. [Faberov et al. J Org Chem USSR 4 153 (English translation) 1968.] |
| Spectrum Detail | Back Directory | [Spectrum Detail]
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride(2421-28-5)MS
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride(2421-28-5)IR1
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride(2421-28-5)IR2
3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride(2421-28-5)Raman
|
|
|