| Identification | More | [Name]
Nifedipine | [CAS]
21829-25-4 | [Synonyms]
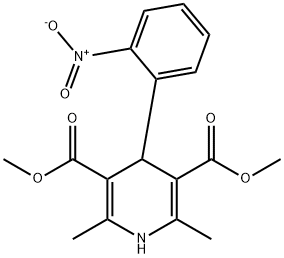
1,4-DIHYDRO-2,6-DIMETHYL-4-(2-NITROPHENYL)-3,5-PYRIDINEDICARBOXYLIC ACID DIMETHYL ESTER
4-(2'-NITROPHENYL)-2,6-DIMETHYL-3,5-DICARBOMETHOXY-1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE
ADALAT
ADALATE
ALDIPIN ANIFED
BAY A 1040
CITILAT
dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
NIFEDIPINE
NIFELAT
1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylicaciddime
3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester
4-(2’-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsaeuredimethy
5-pyridinedicarboxylicacid,1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-dim
Adalat CC
bay1040
corinfar
Dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
Dimethyl 4-(2-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | [EINECS(EC#)]
244-598-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C19H22N2O6 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00057326 | [Molecular Weight]
374.39 | [MOL File]
21829-25-4.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Yellow Crystalline Solid | [Melting point ]
171-175 °C
| [Boiling point ]
481.08°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.2109 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.5486 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
DMSO: soluble
| [form ]
powder
| [pka]
pKa -0.9/>13(DMF,t undefined) (Uncertain) | [color ]
yellow
| [Water Solubility ]
<0.1 g/100 mL at 19.5 ºC | [Usage]
Used as an antihypertensive and antianginal. A dihydorpyridine calcium channel blocker | [Merck ]
6528 | [BCS Class]
2 | [Stability:]
Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions are not stable and must be used within one working day. | [InChIKey]
CYCWGQFQPAYBHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
21829-25-4(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Nifedipine(21829-25-4) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
21829-25-4(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn,Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [WGK Germany ]
1
| [RTECS ]
US7975000
| [HazardClass ]
IRRITANT | [HS Code ]
29333990 | [Hazardous Substances Data]
21829-25-4(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 in mice, rats (mg/kg): 494, 1022 orally; 4.2, 15.5 i.v. (Vater) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
Odorless yellow crystals or powder. Tasteless. | [Reactivity Profile]
NIFEDIPINE(21829-25-4) is sensitive to light. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Aqueous solutions are very sensitive to light. . Insoluble in water. | [Fire Hazard]
Flash point data for this chemical are not available; however, NIFEDIPINE is probably combustible. | [Description]
Nifedipine (21829-25-4) is a clinically useful L-type calcium blocker. | [Originator]
Adalat,Bayer,W. Germany,1975 | [Definition]
ChEBI: Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine, a methyl ester and a C-nitro compound. It has a role as a calcium channel blocker, a vasodilator agent, a tocolytic agent and a human metabolite. | [Manufacturing Process]
45 grams 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, 80 cc acetoacetic acid methyl ester, 75 cc
methanol and 32 cc ammonia are heated under reflux for several hours,
filtered off, cooled and, after suction-filtration, 75 grams of yellow crystals of
MP 172° to 174°C are obtained, according to US Patent 3,485,847. | [Brand name]
Adalat (Bayer); Afeditab (Watson);Procardia (Pfizer). | [Therapeutic Function]
Coronary vasodilator | [World Health Organization (WHO)]
Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It is
listed in the WHO Model List of Essential Drugs. The 10mg tablet is retained on the
list for short-term treatment of hypertension. Sustained-release preparations are
advised for long-term treatment. | [Biological Activity]
L-type calcium channel blocker. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Nifedipine is a L-type Ca2+ channel blocker; and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Nifedipine has neuroprotection activity and protects substantia nigra. Nifedipine has antioxidant potential. Nifedipine downregulates inflammatory cytokines like macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Nifedipine has antihypertensive properties. Nifedipine inhibits extracellular region of adenosine A2a receptor (ADORA2A) gene. | [Mechanism of action]
Nifedipin causes relaxation of smooth musculature, dilation of coronary and peripheral
arteries, and reduction of peripheral resistance and arterial blood pressure, and enhances
oxygen supply to the heart. | [Clinical Use]
The prototype of this class, nifedipine, has potent peripheralvasodilatory properties. It inhibits the voltage-dependentcalcium channel in the vascular smooth muscle but has littleor no direct depressant effect on the SA or AV nodes, eventhough it inhibits calcium current in normal and isolated cardiactissues. Nifedipine is more effective in patients whoseanginal episodes are caused by coronary vasospasm and isused in the treatment of vasospastic angina as well as classicangina pectoris. Because of its strong vasodilatory properties,it is used in selected patients to treat hypertension. | [Synthesis]
Nifedipine, dimethyl ether 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2??-nitrophenyl)-3,5-
piridindicarboxylic acid (19.3.16), is synthesized by a Hantsch synthesis from two
molecules of a |?-dicarbonyl compound?amethyl acetoacetate, using as the aldehyde component?a
2-nitrobenzaldehyde and ammonia. The sequence of the intermediate stages of
synthesis has not been completely established.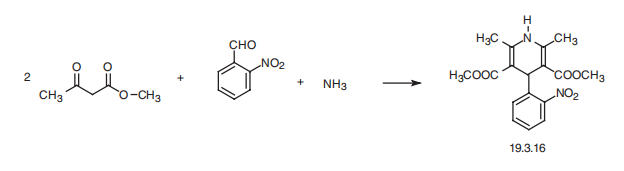
| [Drug interactions]
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline: possibly increases aminophylline
concentration.
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: concentration of dronedarone
increased.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by clarithromycin,
erythromycin and telithromycin.
Antidepressants: metabolism possibly inhibited by
fluoxetine; concentration reduced by St John’s wort;
enhanced hypotensive effect with MAOIs.
Antiepileptics: effect reduced by carbamazepine,
barbiturates, phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: metabolism possibly inhibited by
itraconazole and ketoconazole; concentration
increased by micafungin; negative inotropic effect
possibly increased with itraconazole.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect,
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect of
post-synaptic alpha-blockers; occasionally severe
hypotension and heart failure with beta-blockers.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir; use telaprevir with caution.
Cardiac glycosides: digoxin concentration possibly
increased.
Ciclosporin: may increase ciclosporin level, but not a
problem in practice; nifedipine concentration may be
increased.
Cytotoxics: metabolism of vincristine possibly
reduced.
Grapefruit juice: concentration increased - avoid.
Magnesium salts: profound hypotension with IV
magnesium.
Tacrolimus: increased tacro | [Metabolism]
Nifedipine is metabolised in the gut wall and oxidised in
the liver via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4, to
inactive metabolites.
Excreted mainly as metabolites via the kidney | [storage]
+4°C (desiccate) | [References]
1) Vater et al., (1972), (Pharmacology of 4-(2′-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester (Nifedipine, BAY a 1040); Arzneimittelforschung, 22 1 |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Pharmacological effects]
Nifedipine is a kind of dihydropyridine calcium antagonists, it can inhibit the Ca2 + uptake of cardiac and vascular smooth muscles, and it can expand the coronary artery , increase coronary blood flow,and improve myocardial ischemic tolerance, at the same time, it can expand peripheral arteries and reduce peripheral vascular resistance,and relieve coronary artery spasm, and increase coronary blood flow, improve myocardial ischemia,in order to decrease the blood pressure. Small doses do not affect blood pressure, when expanding coronary artery ,it is a better anti-angina drug .It is used for the prevention and treatment of angina pectoris,with no adverse effects on respiratory function, its efficacy is best particularly for angina pectoris coronary spasm and obstructive airway disease with angina , its efficacy is superior to β-blockers.It is also applied to all types of high blood pressure, including severe and resistant hypertension. Treatment of refractory congestive heart failure may be taking this long. It is also used for the treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension, diffuse esophageal spasm and bronchial asthma, duodenal ulcers, urinary tract obstruction, exercise-induced asthma, achalasia.
Nifedipine has a certain selectivity on vascular smooth muscles , the direct negative inotropic effect and denaturation effect on the heart are weak, systemic administration of it does not cause the heart rate slowing down ,on the contrary, the heart rate performances reflected increase.
The above information is edited by the chemicalbook of Tian Ye.
| [Chemical properties]
Yellow crystals. Melting point 172-174 ℃. Soluble in acetone, chloroform, ethyl acetate, dissolved in hot methanol, insoluble in water. It easily deteriorates in case of light.
| [Uses]
Long-term coronary vasodilators. This product can increase coronary blood flow, reducing myocardial oxygen consumption.it is used for acute and chronic coronary insufficiency,especially the angina and myocardial infarction.
| [Production methods]
O-nitrobenzaldehyde, methyl acetoacetate, methanol, ammonia are refluxed together , then froze , crystallize,after filtration, nifedipine crude is obtained . The crude product is recrystallized through methanol .then the product is derived , yield rate is 50%.
| [Category]
Toxic substances
| [Toxicity grading]
Highly toxic
| [Acute toxicity]
Oral-rat LD50: 1022 mg/kg; Oral-Mouse LD50: 310 mg/kg.
| [Flammability and hazard characteristics]
Combustion produces toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides; medicinal side effects: low blood pressure, cardiac disease, local blood flow disease, high blood sugar, psychosis.
| [Storage Characteristics]
Ventilated , low-temperature, drying; and it is kept separately from food raw materials warehouse.
| [Extinguishing agent]
Dry powder, foam, sand, carbon dioxide, water spray.
|
|
|