| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Fmoc-Lys(Pal-Glu-OtBu)-OH | [CAS]
1491158-62-3 | [Synonyms]
Liraglutide Lys
Fmoc-Lys(Pal-Glu-OtBu)-OH
Fmoc-L-Lys(Palm-L-Glu-OtBu)-OH
(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)MethOxy]Carbonyl Lys(Pal-Glu-OtBu)-OH
N-alpha-(9-Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-N-epsilon-(N-alpha'-palmitoyl-L-glutamic-acid alpha'-t-butyl ester)-L-lysine
L-Lysine, N2-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-N6-[N-(1-oxohexadecyl)-L-γ-glutamyl]-, 1'-(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester
N2-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-N6-[N-(1-oxohexadecyl)-L-gamma-glutamyl]-L-lysine 1'-(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester
(S)-2-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-6-((S)-5-(Tert-Butoxy)-5-Oxo-4-Palmitamidopentanamido)Hexanoic Acid
(2S)-6-[(4S)-5-(tert-butoxy)-4-hexadecanamido-5-oxopentanamido]-2-({[(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy]carbonyl}amino)hexanoic acid
(2S)-2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-6-[[(4S)-4-(hexadecanoylamino)-5-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]hexanoic acid | [Molecular Formula]
C46H69N3O8 | [MDL Number]
MFCD27952849 | [MOL File]
1491158-62-3.mol | [Molecular Weight]
792.06 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Boiling point ]
944.2±65.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.099±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
3.88±0.21(Predicted) | [color ]
White to off-white | [InChIKey]
SUFBOZUGILQOQW-FMQAFZDONA-N | [SMILES]
C(O)(=O)[C@@H](N(C1C2=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C=CC=C2)C(OC)=O)CCCCNC(=O)CC[C@H](NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)C(OC(C)(C)C)=O |&1:3,31,r| |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Fmoc-Lys(Pal-Glu-OtBu)-OH can be used as organic synthesis intermediate and pharmaceutical intermediate, mainly used in laboratory research and development process and chemical production process. | [Application]
Fmoc-Lys(Pal-Glu-OtBu)-OH is a racemic, solid-phase, industrial building block for the synthesis of peptides and polypeptides. This product is used in the synthesis of liraglutide (a peptide), which is used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is synthesized by a solid phase process using coupling reactions with an acid labile linker. This product has been shown to be an efficient building block for the synthesis of peptides and polypeptides that have a sequence that can be varied by changing the protecting group on the amino acid. | [Biological Activity]
ADCs are comprised of an antibody to which is attached an ADC cytotoxin through an ADC linker[1]. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[2]. | [Synthesis]
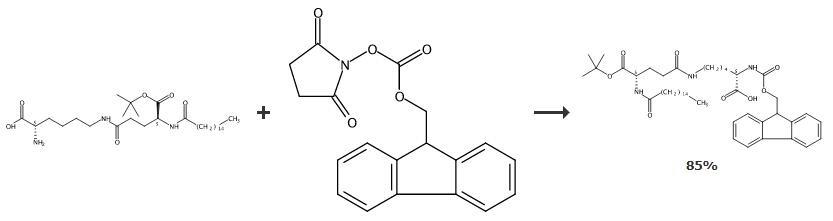
In a flask aqueous sodium carbonate (1.8 g) was prepared followed by addition of THF
(800 mL) and then this mixture was cooled to 0-10 0C. To this mixture, (S)-2-((((9Hfluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)amino)-6-aminohexanoic acid (4.59 g) was added.
Then, a solution of 1 -(tert-butyl) 5-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) palmitoyl-L-glutamate
(corresponding to 5 g of 5-(tert-butoxy)-5-oxo-4-palmitamidopentanoic acid) prepared
according to example 2, was slowly added to above mixture at about 5 0C. The
reaction mixture was stirred for about 2 hours at 25 0C followed by addition of water
(600 mL). The solvents were subjected to distillation and then the pH of the obtained
compound is adjusted to 3.0 using 5N hydrochloric acid. The mixture was stirred for
1-2 hours and resulting solid was isolated filtration, washing with water (30 mL). The
obtained solid was dried under vacuum for 8 hours at about 45°C to afford title
compound in -85% yield. | [References]
[1] Beck A, et al. Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(5):315-337.
[2] Nalawansha DA, et al. PROTACs: An Emerging Therapeutic Modality in Precision Medicine. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27(8):998-985. |
|
|