| Identification | More | [Name]
Ammonium bicarbonate | [CAS]
1066-33-7 | [Synonyms]
AMMONIUM ACID CARBONATE
AMMONIUM BICARBONATE
AMMONIUM CARBONATE
AMMONIUM CARBONATE, ACIDIC
AMMONIUM CARBONATE TS
AMMONIUM HYDROGEN CARBONATE
CARBONIC ACID MONOAMMONIUM SALT
acidammoniumcarbonate
ammoniumbicarbonate(1:1)
monoammoniumcarbonate
AMMONIUM BICARBONATE , FOOD GRADE
Ammonium bicarbonate
acid ammonium carbonate
Ammonium acid carbonate
Ammonium hydrogen carbonate
AMMONIUM BICARBONATE, REAGENTPLUS TM, >= 99.0%
DEGLYCOSYLATION 10X REACTION BUFFER
2,6'-TDI, Oekanal
Ammonium bicarbonate, Eluent additive for LC-MS
AmmoniumBicarbonateFcc
AmmoniumBicarbonate(Nh4)Hco3
AmmoniumHydrogenCarbonate,>99%
AmmoniumBicarbonateAr | [EINECS(EC#)]
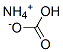
213-911-5 | [Molecular Formula]
CH5NO3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00012138 | [Molecular Weight]
79.06 | [MOL File]
1066-33-7.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Ammonium bicarbonate is a white crystalline
solid with a faint ammonia odor. | [Melting point ]
105 °C
| [Boiling point ]
143.04°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1,586 g/cm3 | [vapor density ]
2.7 (vs air)
| [vapor pressure ]
67 hPa (20 °C) | [refractive index ]
1.4164 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
Store at RT. | [solubility ]
H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
| [form ]
Solid | [color ]
White | [Odor]
faint ammonia odor | [PH]
7.0-8.5 (25℃, 1M in H2O) | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, alkali metals. | [Water Solubility ]
220 g/L (20 ºC) | [λmax]
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.030
λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.020 | [Merck ]
14,497 | [BRN ]
4329606 | [LogP]
-0.809 (est) | [Uses]
White crystals made by carbonate salts acting upon ammonium
hydroxide followed by crystallization. Also known as
hartshorn and rock ammonia, ammonium bicarbonate is
soluble in water but decomposes when heated. It was used
in place of ammonia when making ammonia-ripened gelatin
emulsions. | [Dissociation constant]
6.49 at 20℃ | [CAS DataBase Reference]
1066-33-7(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
1066-33-7(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn,Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S22:Do not breathe dust . | [WGK Germany ]
1
| [RTECS ]
BO8600000
| [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
28369990 | [Safety Profile]
Poison by intravenous route. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NO, and NH3 | [Hazardous Substances Data]
1066-33-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 orally in Rabbit: 1576 mg/kg |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
A white crystalline solid having the odor of ammonia. Soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Used to make other ammonium compounds, in food processing, and for other uses. | [Reactivity Profile]
Heat > 36°C ( produces ammonia and carbon dioxide); strong acids and strong bases (CO2 and NH3) [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980 p. 141]. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Soluble in water. | [Hazard]
Evolves irritating fumes on heating to 35C.
| [Health Hazard]
Inhalation may cause respiratory irritation. Ingestion could be harmful. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation. | [Potential Exposure]
It is used in leavening for some baked
goods; in baking powders and fire extinguishers; to make
dyes and pigments; in the manufacture of porous plastics;
and as an expectorant. | [First aid]
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any
contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least
15 minutes, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek
medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately
with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately.
If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from
exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions,
including resuscitation mask) if breathing has
stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer
promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical
has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large
quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an
unconscious person vomit. | [Shipping]
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances,
solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous
material, Technical Name Required. | [Incompatibilities]
Contact with strong caustics, such as
potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide will cause the
release of ammonia gas. Decomposes as temperature rises
>35 C. | [Waste Disposal]
May be buried in a chemical
waste landfill. If neutralized ammonium bicarbonate is
amenable to treatment at a municipal sewage treatment
plant. | [Physical properties]
White crystalline solid; prismatic crystal; faint odor of ammonia; stable at ambient temperature but decomposes on heating at 60°C; melts at 107.5°C on very rapid heating; density 1.586 g/cm3; vapor pressure 435 torr at 25°C; readily dissolves in water (21.6g/100g at 20°C, and 36.6g/100g at 40°C). | [Definition]
ChEBI: Ammonium bicarbonate is an organooxygen compound. | [Agricultural Uses]
Ammonium hydrogen carbonate is another name for ammonium bicarbonate (NH4CO3), It is a low nitrogen containing fertilizer (17% N), used largely in China. It is produced by heating ammonium hydroxide with excess carbon dioxide, followed by evaporation of water. |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [description]
Ammonium bicarbonate(1066-33-7) is a commonly used reagent for industrial and research procedures. Ammonium bicarbonate is volatile in solution and releases ammonia and CO2. This property makes ammonium bicarbonate a good buffer for such applications as lyophilization and matrix assisted laser desorption. Ammonium bicarbonate is also utilized for the in-gel digestion of proteins by trypsin and in the MALDI mass spectrometric analysis of proteins.

Ammonium bicarbonate is used as a baking powder, in some food processing applications, in cough syrups and as antacid. It also has uses as a fertilizer, pH buffer, and reagent in chemical laboratories. In the industry, it is used in the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, catalysts, ceramics, fire-retardants, plastics and other products.
| [Nitrogen fertilizer]
Ammonium bicarbonate is mainly used as fertilizers. After being applied to the soil, the ammonium ion (NH4 +) contained in ammonium bicarbonate can be absorbed by soil colloid or lattice-fixed or transformed into nitrate nitrogen. After being absorbed by plants, there are no accessory constituents remaining in the soil with a small impact on the soil pH. It is applicable to all kinds of soil and crops, soil without leaving any harmful substance residue for the soil and crops. It is quick-acting nitrogen fertilizer and can be subject to long-term usage.
In order to prevent the loss of fertilizer efficacy due to ammonia volatilization and the burning of the crop stems and leaves, we can apply deep placement and cover soil. It can be used as basic fertilizer for topdressing, but not suitable to be used as seed manure. When being used for topdressing, we should prevent the drop of ammonium bicarbonate onto the plant, to avoid ammonia hazards. The shortcoming of ammonium bicarbonate as a fertilizer lies in its chemical instability. After the addition of crystalline modifier, the crystal of ammonium bicarbonate is enlarged and the water content is reduced, reducing the phenomenon of easily subjecting to decomposition and agglomeration. Ammonium bicarbonate is one of nitrogen fertilizer industrial products, being the major varieties of small nitrogenous fertilizer plants in China, being one of the purification products of coke oven in the coking plant. Coking plant takes concentrated ammonia as raw materials for reaction with carbon dioxide to generate ammonium bicarbonate crystals with centrifugal filtering to obtain ammonium bicarbonate products.
Ammonium bicarbonate is easy to be subject to decomposition. It is appropriate to be packed with the combination of inner plastic film and external plastic bag or 3-layers of kraft paper sacks, both need to be sealed and stored in a warehouse of being cool, low-temperature, dry and ventilated to prevent moisture, rain and sun. | [Chemical properties]
Ammonium bicarbonate appears as white monoclinic or orthorhombic crystals. It is soluble in water, but insoluble in ethanol, carbon disulfide and concentrated ammonia.
It dissolves in water to give a mildly alkaline solution. It is insoluble in most organic solvents. While it is stable at room temperature (25 °C), it decomposes at temperatures above 36 °C to form ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water in an endothermic reaction (absorbs energy for the reaction from the surroundings).
NH4HCO3 → NH3 + CO2 + H2O
Ammonium bicarbonate reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide, and reacts with bases to produce ammonia.
| [Uses]
1. Ammonium bicarbonate(1066-33-7) is used as nitrogen fertilizer, being applicable to a variety of soils, can simultaneously provide the ammonium nitrogen and carbon dioxide demanded by crop growth. However, it contains low nitrogen content and is also easy to caking.
2. It can be used as analytical reagent as well as being used in synthesizing ammonium salt and fabric degreasing.
3. It can promote crop growth and photosynthesis; trigger seedlings and the growth of leaves. It can be used as topdressing as well as being directly applied as ground fertilizer as food leavening agent and bulking agent.
4. Ammonium bicarbonate can be used as a senior food fermentation agent. Its combination with sodium bicarbonate can be used as the raw materials of leavening agent such as bread, biscuits and pancakes. It can also be used as raw material of foam powder juice, as well as being used for the blanching of green vegetables and bamboo shoots. Moreover, it can be used as medicine and reagents.
5. Alkali; leavening agent; buffer; aerating agent.
Its combination with sodium bicarbonate can be used as the raw materials of leavening agent such as bread, biscuits and pancakes. Baking powder also takes this product as the main ingredient, together with the acidic substances. It can also be used as raw material of foam powder juice. The dosage of the blanching of green vegetables and bamboo shoots should be 0.1% to 0.3%.
6. It can be used as analytical reagent; used for ammonium salt synthesis. Pharmaceuticals; baking powder; dyeing; It can be used for fabric degreasing. It can also be used as foamed plastics.
| [Production method]
Send the compressed carbon dioxide into the concentrated ammonia, and place it under the carbon dioxide pressure; simultaneously apply cooling; precipitate out the crystal; followed by centrifugal separation and dehydration to obtain the final product. Upon refining, dissolve it in water, and add ethanol to re-crystallize it.
Carbonization method: after the ammonia is absorbed by water; apply carbon dioxide for carbonization, followed by separation and drying to produce ammonium bicarbonate.
NH3 + CO2 + H2O → NH4HCO3
To the carbon dioxide gas originated from the lime kiln and be subject to cleaning and washing, send the ammonia to saturation, followed by centrifugal separation and hot air drying to obtain the finished products.
NH3 + CO2 + H2O → NH4HCO3
|
|
|