
N-Methyldidecylamine synthesis
- Product Name:N-Methyldidecylamine
- CAS Number:7396-58-9
- Molecular formula:C21H45N
- Molecular Weight:311.59

112-30-1
480 suppliers
$5.00/25g
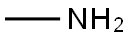
74-89-5
7 suppliers
$13.44/25ML

7396-58-9
156 suppliers
$30.00/25mL
Yield: 94.7%
Reaction Conditions:
with hydrogen at 195; under 772.577 - 1200.12 Torr; for 4.1 h;
Steps:
4
General procedure: A 1 L flask was charged with an aqueous solution prepared by dissolving copper nitrate, nickel nitrate and ruthenium chloride in water such that the molar ratio therebetween in terms of the respective metal atoms (Cu:Ni:Ru) is 4:1:0.01, and the aqueous solution was heated while stirring. When reaching a temperature of 50° C., zeolite was charged into the flask, and further when reaching a temperature of 90° C., a 10% by weight sodium carbonate aqueous solution was gradually dropped therein. The resulting mixture was aged for 1 h, and the obtained precipitate was separated by filtration, washed with water and then dried, and thereafter calcined at 600° C. for 3 h to thereby prepare a Cu-Ni-Ru/zeolite catalyst (molar ratio between the respective metal atoms: Cu:Ni:Ru=4:1:0.01). The thus prepared catalyst was added to the raw alcohol in the first reaction vessel in an amount of 0.14% by weight on the basis of the weight of the raw alcohol. While stirring the resulting solution at 950 r/min, hydrogen was introduced into the flask at a flow rate of 36 NL/h using a circulating pump, and circulated through a series of reaction processes constructed from the first reaction vessel and the below-mentioned second reaction vessel. The contents of the first reaction vessel were heated to a temperature at which the catalyst was able to be reduced, and held at that temperature for a predetermined time to reduce the catalyst. After completion of reduction of the catalyst, a mixture of dimethyl amine and a hydrogen gas was introduced into the reaction system. The reaction system was gradually heated to 225° C. and subjected to amination reaction while maintaining a temperature of 225° C. The reaction was appropriately monitored and traced by gas chromatography. The reaction was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the raw alcohol and the raw amine were replaced with decyl alcohol and monomethyl amine, respectively, and the reaction temperature, the concentration of the catalyst based on the raw alcohol and the hydrogen flow rate were changed to 195° C., 1.2% by weight and 18 NL/h, respectively. The results are shown in Table 3. The amount of hydrogen used in the reaction of Example 4 was 24.1 L. Assuming that the reaction was conducted without recovering hydrogen, an estimated amount of the hydrogen gas flowing through the reaction system was 74 L. In addition, from the results of Examples 3 and 4, it was confirmed that according to the production process of the present invention, it was possible to produce various tertiary amines with a high yield and a high selectivity.
References:
KAO CORPORATION;Watanabe, Masahiko;Tateno, Gosuke;Mizukoshi, Hirofumi US2013/289309, 2013, A1 Location in patent:Paragraph 0104-0106; 0119-0121

23220-25-9
4 suppliers
inquiry

112-30-1
480 suppliers
$5.00/25g

7516-82-7
23 suppliers
inquiry

7396-58-9
156 suppliers
$30.00/25mL
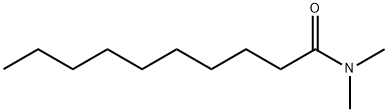
14433-76-2
304 suppliers
$9.00/25g

112-30-1
480 suppliers
$5.00/25g

7516-82-7
23 suppliers
inquiry
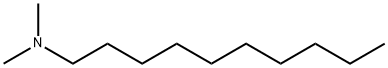
1120-24-7
165 suppliers
$5.00/25g

7396-58-9
156 suppliers
$30.00/25mL

14433-76-2
304 suppliers
$9.00/25g

112-30-1
480 suppliers
$5.00/25g

1120-24-7
165 suppliers
$5.00/25g

7396-58-9
156 suppliers
$30.00/25mL