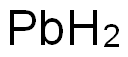
Lead synthesis
- Product Name:Lead
- CAS Number:7439-92-1
- Molecular formula:Pb
- Molecular Weight:207.2
Lead also occurs in various uranium and thorium minerals, arising directly from radioactive decay. Because certain isotopes are concentrated in lead derivatives from such sources, both the atomic weight and the density of the samples vary significantly from normal lead. Lead ores generally occur in nature in association with silver and zinc. Other metals commonly occurring with lead ores are copper, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Most of the world production of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth is a result of their separation from lead ores. Commercial lead ores may contain as little as 3% lead, but a lead content of 10% is most common. The ores are concentrated to ≥ 40% lead content before smelting. A variety of mechanical separation processes may be employed for the concentration of lead ores, but the sulfide ores are generally concentrated by flotation processes.
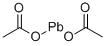
301-04-2
175 suppliers
$21.00/1G
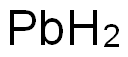
7439-92-1
250 suppliers
$16.17/100g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with aluminium in water;byproducts: H2; slow react.; faster react. on addn. of KCl;;
References:
Senderens, J.-B. [1897,vol. 17,p. 271 - 286] [Gmelin Handbuch der Anorganischen Chemie,Gmelin Handbook: Pb: MVol.C2, 195, page 759 - 760]
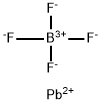
13814-96-5
130 suppliers
$70.00/50g
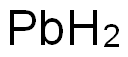
7439-92-1
250 suppliers
$16.17/100g