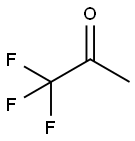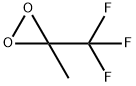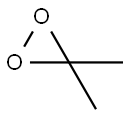
dimethyldioxirane synthesis
- Product Name:dimethyldioxirane
- CAS Number:74087-85-7
- Molecular formula:C3H6O2
- Molecular Weight:74.08
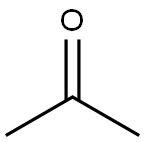
67-64-1
0 suppliers
$17.30/10ml

74087-85-7
11 suppliers
inquiry
Yield:74087-85-7 3.8%
Reaction Conditions:
with oxone;sodium hydrogencarbonate in water at 0 - 25; under 75.0075 - 750.075 Torr; for 0.716667 - 0.766667 h;Product distribution / selectivity;
Steps:
1; 2; 3; 4; 5
EXAMPLE 1; The following components were metered separately and continuously to the lower third of a bubble column which was operated at 20° C. and 0.3 bar absolute and had an internal diameter of 40 mm, a height of 630 mm and an empty pipe volume of approx. 0.79 l: 1) a 9.75% by weight aqueous potassium hydrogenmonopersulfate solution with a mass flow rate of 95.2 g/h, corresponding to 0.061 mol/h of hydrogenmonopersulfate, prepared from the triple salt [2 KHSO5.KHSO4.K2SO5] and water, 2) 158.7 g/h of a 7.06% by weight aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate solution, 3) 414.2 g/h of a 57% by weight acetone solution in water comprising 400 ppm of n-dodecane as a defoamer and 4) via a frit, 180 l (STP)/h of nitrogen. The potassium hydrogenmonopersulfate content of the aqueous solution was determined by iodometric titration shortly before use. From the bubble column, 478 g/h of a water-rich liquid and also a dioxirane-containing gas phase were withdrawn continuously. This gas phase was conducted through a very efficient cooler operated at -30° C. The cooler was dimensioned such that components having a boiling point above -20° C. were virtually fully condensable. After the condensation, 173.5 g/h of a solution comprising dioxirane, with 0.69% by weight of dimethyldioxirane and 8.3% by weight of water, and also a gas phase were obtained.The dimethyldioxirane yield was 26.5% based on the hydrogenmonopersulfate.The proportion of liquid in the bubble column was measured at the end of the experiment and was 60% by volume. This corresponds to a residence time of the liquid phase in the reactor of approx. 43 min. The normalized condensate mass flow rate was approx. 2844 g of condensate/mole of active oxygen.; EXAMPLE 2; Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, 1) 90.0 g/h of a 5.74% by weight aqueous potassium hydrogenmonopersulfate solution, corresponding to 0.034 mol/h of hydrogenmonopersulfate, which was prepared in the same way as described under Example 1, 2) 155.7 g/h of a 3.53% by weight aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate solution, 3) 413.8 g/h of a 57% by weight aqueous acetone solution comprising 400 ppm of dodecane as a defoamer and 4) via a frit, 180 l (STP)/h of nitrogen were fed to the same bubble column as described under Example 1. From the bubble column, 472.7 g/h of a water-rich liquid and also a dioxirane-containing gas phase were withdrawn continuously. As described under Example 1, this gas phase was partially condensed to obtain 172.7 g/h of a solution comprising dimethyldioxirane with 0.46% by weight of dimethyldioxirane, and also a gas phase.This corresponds to a dimethyldioxirane yield of 31.5% based on hydrogenmonopersulfate.The proportion of liquid in the bubble column was measured at 62% by volume at the end of the experiment, corresponding to a residence time of the liquid phase in the reactor of approx. 45 min.The normalized condensate mass flow rate in this example was approx. 5080 g of condensate/mole of active oxygen.; EXAMPLE 3; The following components were metered continuously to the upper end of a bubble-cap tray column which was operated at 25° C. and 1 bar absolute and had 8 trays, a height of 800 mm and an internal diameter of 50 mm: 1) 23.9 g/h of a 9.59% by weight aqueous potassium hydrogemnonopersulfate solution, corresponding to 0.015 mol/h of hydrogenmonopersulfate, which was prepared in the same way as in Example 1, 2) 39.5 g/h of a 7.06% by weight aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate solution, and 3) 85.6 g/h of a 57% by weight aqueous acetone solution. At the same time, 200 l (STP)/h of nitrogen were metered in at the lower end of the bubble-cap tray column.From the bubble-cap tray column, 96.8 g/h of a water-rich liquid were withdrawn continuously from the lower region thereof, and a gas phase comprising dioxirane from the upper region thereof. In a corresponding manner to Example 1, the gas phase was passed through a cooler to obtain 44.1 g/h of a solution comprising dimethyldioxirane, corresponding to 0.56% by weight of dimethyldioxirane, and also a gas phase. The dimethyldioxirane yield based on potassium hydrogenmonopersulfate was 22%.In this example, the normalized condensate mass flow rate was approx. 2940 g of condensate/mole of active oxygen.; EXAMPLE 4; A distillation column having an internal diameter of 30 mm, a height of 370 mm, charged with 5×5 mm glass Raschig rings was attached to the upper section of the bubble column described in Example 1. The reflux ratio was controlled via the temperature of a cooler at the top of the column (-10° C.). The reaction was operated under the same operating conditions as described under Example 1, i.e. at 20° C. and 0.3 bar absolute.At the lower third of the bubble column, the following components were fed in continuously: 1) a 9.84% by weight aqueous potassium hydrogenmonopersulfate solution with a mass flow rate of 94.8 g/h, corresponding to 0.0613 mol/h of hydrogenmonopersulfate, prepared from the triple salt [2KHSO5.KHSO4.K2SO5] and water, 2) 157.3 g/h of a 7.06% by weight aqueous sodium hydrogencarbonate solution, 3) 414.9 g/h of a 57% by weight acetone solution in water comprising 400 ppm of dodecane, and 4) via a frit, 180 l (STP)/h of nitrogen. From the bubble column, 152.0 g/h of a water-rich liquid and a dioxirane-containing gas phase were withdrawn continuously. The gas phase was conducted through the same cooler as described under Example 1. After partial condensation in the cooler, 173.5 g/h of a solution comprising dimethyldioxirane with 0.72% by weight of dimethyldioxirane (determined by iodometric titration) and 0.6% by weight of water (determined by standard Karl-Fischer titration), and also a gas phase comprising uncondensable constituent were obtained.The dimethyldioxirane yield was 24% based on the hydrogenmonopersulfate used.The liquid fraction in the bubble column was measured at the end of the experiment and was 64% by volume; this corresponds to a residence time of the liquid phase in the reactor of approx. 46 min.The normalized condensate mass flow rate was approx. 2490 g of condensate/mole of active oxygen.; COMPARATIVE EXAMPLE; In a semibatch process, a 4 l four-neck flask was initially charged with 635 g of water, 380 g of acetone and 145 g of sodium hydrogencarbonate.The heterogeneous (liquid/solid) mixture was cooled to from 0 to 5° C.At this temperature, the triple salt [2KHSO5.KHSO4.K2SO5], 300 g, corresponding to approx. 0.976 mol of hydrogenmonopersulfate, were added as a solid slowly and in portions via a solid metering unit.The mixture was warmed to room temperature and a solution comprising dimethyldioxirane was subsequently distilled off with intensive stirring at 100 mbar and 25° C.The dimethyldioxirane solution was isolated with the aid of a series of cold traps cooled to -78° C.Within 80 min, after combination of the fractions obtained, 292.1 g of solution were isolated. The iodometric titration of this solution gave 0.93% by weight of dimethyldioxirane with, correspondingly, a total of 0.0367 mol of dimethyldioxirane. This corresponds to a dimethyldioxirane yield based on the hydrogenmonopersulfate used of approx. 3.8%. The comparative example was carried out analogously to the method of Adam in Chem. Ber. 1991, 124, 2377.The mean normalized condensate mass flow rate was 299 g of condensate/mole of active oxygen.
References:
Basf Aktiengesellschaft US2008/177092, 2008, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 4-5
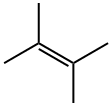
563-79-1
147 suppliers
$29.00/5mL
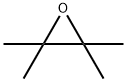
5076-20-0
16 suppliers
$77.09/5g
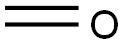
50-00-0
894 suppliers
$10.00/25g
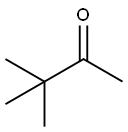
75-97-8
245 suppliers
$10.00/1g

74087-85-7
11 suppliers
inquiry
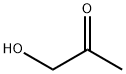
116-09-6
271 suppliers
$11.00/25g

67-64-1
0 suppliers
$17.30/10ml