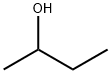
The brief introduction of 2-Butanol
May 30,2024
Introduction
Alcohols are emitted into the atmosphere by different natural and anthropogenic sources. These organic volatile compounds are also produced in the atmosphere from the photooxidation of alkanes initiated by hydroxyl (OH) radicals. Some studies showed that solvent use is central Europe's primary emission source of these oxygenated hydrocarbons. However, the emission of 2-butanol by agricultural and natural plant species has also been measured by Konig et al. 2-butanol has been proposed as a candidate for addition to the Clean Air Act list of hazardous air pollutants[1]. The atmospheric chemical degradation of alcohols is expected to be their OH-initiated reaction and, to a lesser extent, their reaction with NO3.
Information
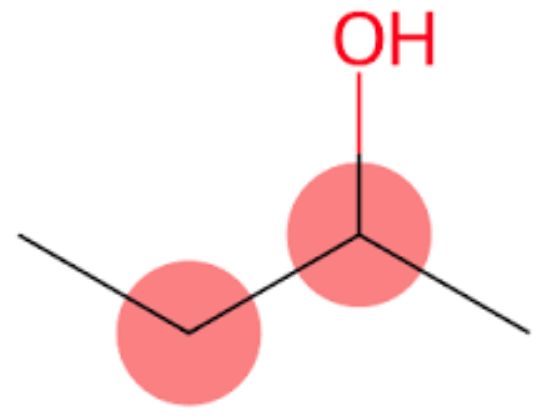
2-Butanol, also known as 2-butyl alcohol or 2-hydroxybutane, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohols are compounds containing a secondary alcohol functional group, with the general structure HOC(R)(R') (R, R'=alkyl, aryl). 2-Butanol is an odourless-tasting compound. In addition, Butan-2-ol and 2-butanol are the same. IUPAC suggested naming us butane-2-ol, but generally, it is written as 2-butanol, and it is accepted by IUPAC, too. It is found in many foods, including highbush blueberry, milk and milk products, rosemary, and tea.
Uses
2-Butanol is commonly used as a flavouring agent. This secondary alcohol is a flammable, colourless liquid that is soluble in 12 parts water and completely miscible with polar organic solvents such as ethers and other alcohols. It is produced on a large scale, primarily as a precursor to the industrial solvent methyl ethyl ketone. 2-Butanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(-)-2-butanol and (S)-(+)-2-butanol. It is normally found as an equal mixture of the two stereoisomers — a racemic mixture.
References
[1] Elena Jiménez. “Atmospheric Degradation of 2-Butanol, 2-Methyl-2-butanol, and 2,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol: OH Kinetics and UV Absorption Cross Sections.” The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 109 48 (2005): 10903–10909.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Main Differences between 1 Butanol and 2 Butanol Nov 24, 2022
The passage introduces the differences between 1 Butanol and 2 Butanol, also mentions the intermolecular forces of 2 Butanol.
- Production and properties of 2-Butanol Apr 13, 2022
2-Butanol (C4H10O) is one of the four isomers of butanol .
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025APICadmium is a soft, silvery-white metal. It has 48 electrons arranged in an electronic configuration of [Kr]4d105s2.....
May 30,2024Inorganic chemistry