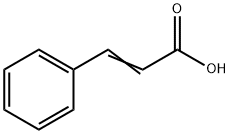
Cinnamic Acid: Properties, Composition, and Applications in Modern Chemistry
May 14,2024
Introduction
Cinnamic acid, a key aromatic compound in the world of organic chemistry, continues to attract significant attention due to its extensive applications and role in various chemical reactions. Structurally known as phenyl acrylic acid, cinnamic acid is an organic compound that represents an important building block in the synthesis of a myriad of other chemicals. This naturally occurring substance not only is pivotal in plant metabolism—contributing to the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids—but also has notable implications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. Its ability to integrate into multiple chemical pathways makes it a substance of great interest for both academic research and industrial applications, inviting ongoing exploration and utilization.

Figure 1 Characteristics of Cinnamic acid
Properties
Cinnamic acid, with the chemical formula C9H8O2, possesses distinctive properties that define its utility in various applications. Its crystalline nature imbues it with a characteristic appearance, often manifesting as white to pale yellow crystals. Notably, its melting point, spanning from 133°C to 136°C, underscores its stability under specific temperature conditions.
In terms of solubility, cinnamic acid exhibits a modest affinity for water, yet its compatibility with organic solvents like ethanol and diethyl ether is noteworthy due to its higher solubility in these mediums. This feature enhances its versatility in diverse chemical processes and formulations.
Moreover, its molecular structure, punctuated by a double bond, endows it with reactive potential, facilitating its involvement in a myriad of addition reactions. This reactivity renders cinnamic acid a cornerstone in synthetic chemistry, enabling the synthesis of various compounds pivotal in pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and agrochemicals, among other industries. Thus, cinnamic acid stands as a prime example of a compound whose properties catalyze innovation and advancement across multiple domains.
Main Constituents
The compound primarily consists of a benzene ring attached to an acrylic acid group, which allows it to act as a precursor in the biosynthesis of flavonoids and lignin in plants. In industrial contexts, cinnamic acid can be synthesized through several methods, including the Perkin reaction, which involves the reaction of benzaldehyde with acetic anhydride in the presence of an alkali metal acetate. This synthesis underscores its adaptability and utility in creating complex molecular structures.
Uses
Cinnamic acid’s applications are diverse and impactful across multiple sectors. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is utilized as a precursor in the synthesis of essential drugs such as the anticoagulant warfarin and various antifungal agents. Its antimicrobial properties make it useful in preserving food products and in cosmetic formulations to prevent microbial growth.
Furthermore, cinnamic acid serves as a starting material in the manufacture of flavors and fragrances, imparting a spicy, cinnamon-like aroma that is highly valued in perfumes and essential oils. In addition to its role in flavor and fragrance chemistry, it is instrumental in the production of various polymers and plastics, showcasing its role in enhancing material properties and functionality[2].
Precautions
Handling cinnamic acid requires careful consideration due to its reactive nature. It should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation. Protective equipment such as gloves and eye protection should be worn when handling the chemical to avoid irritation, as it can be hazardous if it comes into contact with skin or eyes. Additionally, proper ventilation must be maintained during its use to prevent inhalation of any fumes that may be released during chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Cinnamic acid is a compound of remarkable versatility and utility in the field of chemistry. Its multifaceted roles range from pharmaceutical applications to flavor enhancements and polymer chemistry, underscoring its importance in both natural and synthetic contexts. As research continues to reveal new uses and synthetic methods, cinnamic acid remains a focal point for innovation and application in modern chemistry. Understanding its properties, safe handling practices and applications can help professionals exploit its benefits while minimizing risks associated with its use.
References
[1]Ruwizhi N, Aderibigbe B A. Cinnamic acid derivatives and their biological efficacy[J]. International journal of molecular sciences, 2020, 21(16): 5712.
[2]Prateek S. Cinnamic acid derivatives: a new chapter of various pharmacological activities[J]. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2011, 3(2): 403-423.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Cinnamic Acid: Dietary Sources, Mechanisms of Action and New Formulation Jan 9, 2024
Cinnamic acid in plant-based foods stimulates insulin secretion, but its limited bioavailability led to new formulations like nanoparticles for improved effectiveness against chronic diseases.
- Cinnamic acid: Toxicity, Pharmacokinetics and Application Apr 14, 2023
Cinnamic acid is an unsaturated carboxylic acid, and is used in flavorings, synthetic indigo, and certain pharmaceuticals.
Cinnamic acid
621-82-9You may like
- Cinnamic acid
-

- $41.00 / 100mg
- 2025-05-15
- CAS:621-82-9
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.74%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Cinnamic acid
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2025-05-15
- CAS:621-82-9
- Min. Order: 7kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 10000
- Cinnamic acid
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-05-15
- CAS:621-82-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%min
- Supply Ability: 25tons/month