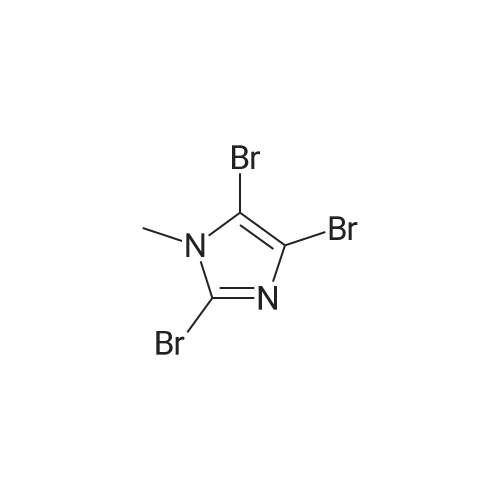
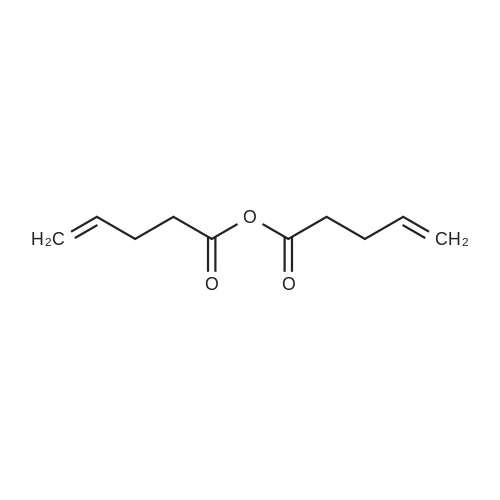
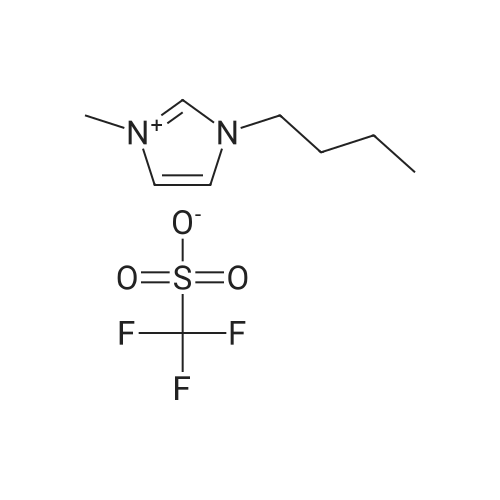
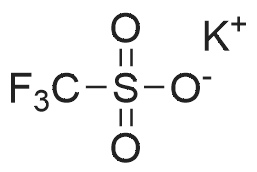
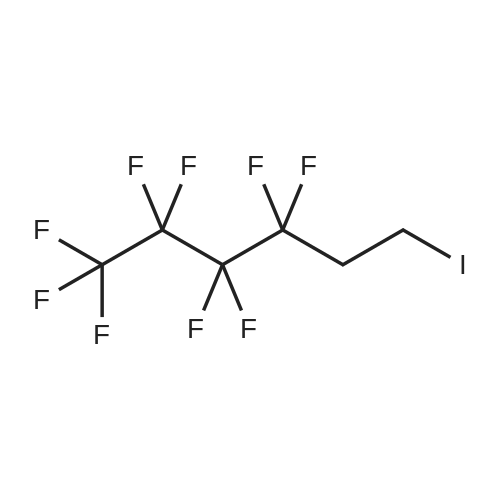
| 29% |
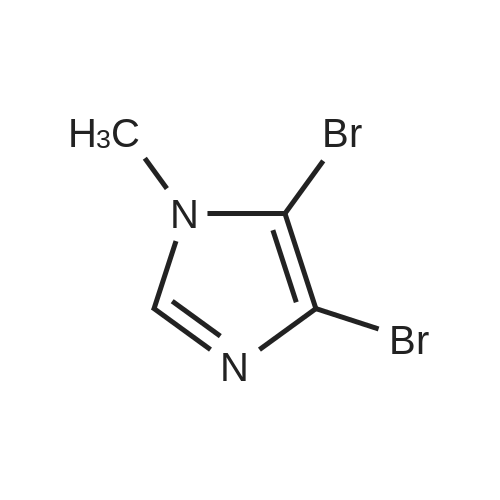
With bromine; sodium acetate; In acetic acid; at 20℃; for 2.5h; |
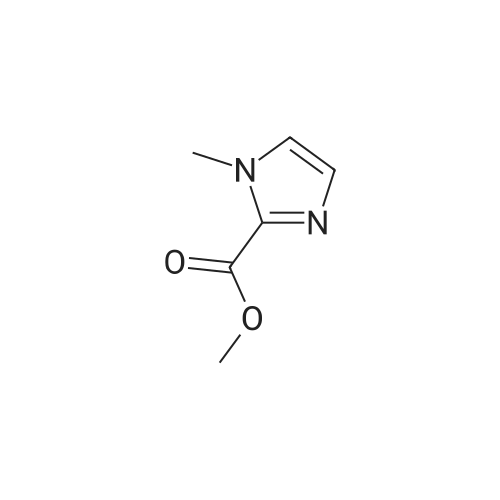
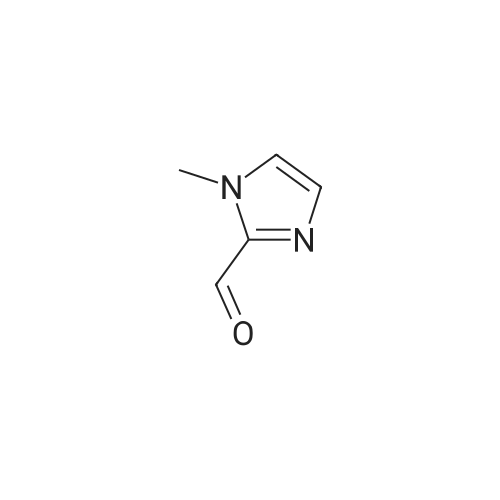
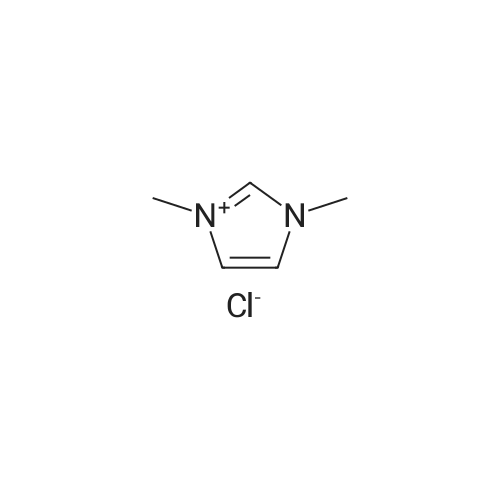
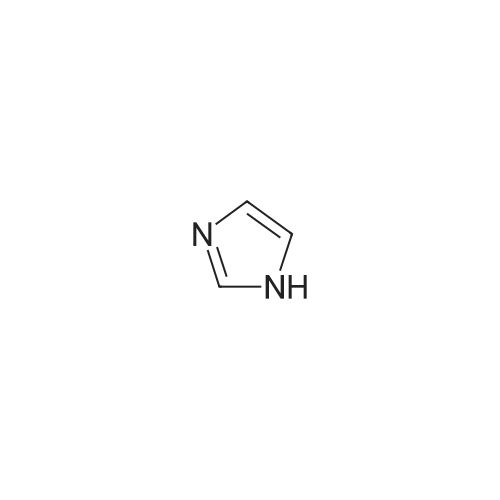
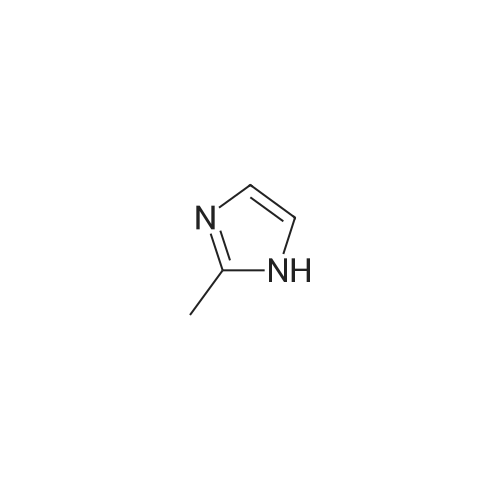
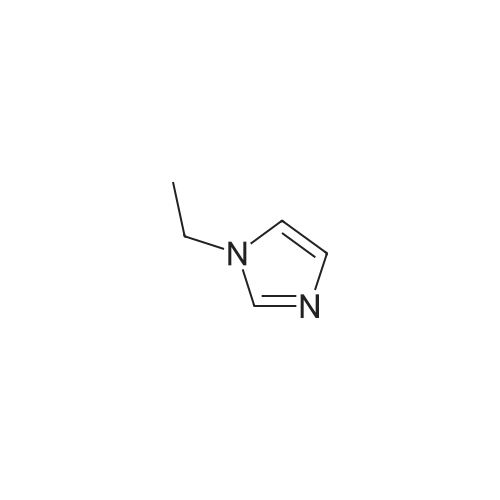
To a solution of N-methylimidazole (1.64 g, 19.97 mmol) and sodium acetate (25 g, 300 mmol) in acetic acid (180 mL) at room temperature was added bromine (9.6 g, 60.07 mmol) dropwise as a solution in 20 mL acetic acid. The resulting mixture was stirred for 2.5 h at room temperature. Acetic acid was removed in vacuo, the residue was suspended in 500 mL water and stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The resultant precipitate was filtered, washed with water and dried under high vacuum to give 2,4,5-tribromo-l-methyl- lH-imidazole (1.82 g, 29percent - some product remained in the mother liquor) as a light yellow powder. Used without further characterization. To a suspension of the tribromide (1.82 g, 5.71 mmol) in 45 mL water was added sodium sulfite (13 g, 103 mmol) and the resulting mixture was stirred at rapid reflux for 24 h. After cooling to room temperature, organics were extracted with ether (3 chi 75 mL), dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated to give 1.61 g of a mixture of tri-, di- and monobromoimidazoles. This mixture was re-subjected to the reduction conditions (same quantity of sodium sulfite) using 15 mL of 3: 1 water/acetic acid as solvent and heating in a sealed vessel at 130 °C for 60 h. After cooling to room temperature, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 9-10 by addition of 2 N sodium hydroxide. Organics were extracted with ether (3 chi 50 mL), dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated to give crude 4-bromo-l -methyl- lH-imidazole (571 mg, ca. 62percent). Used without further characterization.. 4-Butyl-l -methyl- lH-imidazole (95 mg, 22 percent) was synthesized as in Example 3.1 using 4-bromo-l -methyl- lH-imidazole (571 mg, ca. 3.53 mmol) in place of 5-bromo-2- formylfuran and propylboronic acid (372 mg, 4.24 mmol) in place of hexylboronic acid. Used without further characterization. To a solution of diisopropylamine (0.13 mL, 0.918 mmol) in 2 mL anhydrous tetrahydrofuran at - 0°C was added -butyllithium (0.34 mL, 2.5 M in hexanes) dropwise. The solution was stirred while warming to -20 °C over 20 minutes. After cooling to -78 °C, 4-butyl-l -methyl- lH-imidazole (95 mg, 0.765 mmol) was added dropwise as a solution in 2 mL anhydrous tetrahydrofuran. The resulting solution was stirred for 40 minutes at -78 °C. Dimethylformamide (0.24 mL, 3.06 mmol) was added and the solution stirred while warming to room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into 15 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid and stirred for 5 minutes. The pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to 7-8 by careful addition of saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. Organics were extracted with dichloromethane (3 chi 20 mL), dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The crude residue was subjected to chromatography on silica gel with gradient elution (5-50percent ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give l -methyl-4-propyl-lH-imidazole-2-carbaldehyde (9 mg, 8percent) as an off-white solid. Used without further characterization |
| 63.76 g |
With N-Bromosuccinimide; In chloroform; at 20℃; for 1.5h; |
2-(2-Ethynyl-1 -methyl-1 H-imidazol-4-yl)-thiazole ? ?To a solution of compound N-methylimidazole (65.6 g, 0.8 mol) in CHCl3 (1 .5 L), N-bromosuccinimide (NBS; 476g,2.4 mol) was added in portion and then the mixture was stirred at roomtemperature for 1 .5 hour, filtered and concentrated, the residue was purifiedby column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: EA/PE 1/10) to afford 2,4,5-Tribromo-1 -methyl-1H-imidazole (63.76 g, 0.2 mol), which was dissolved in in dry THF (2L) andEtMgBr (220 ml_, 0.22 mol) was added slowly under N2 atmosphere at ambient temperature during 3 hourand stirred for another 2 hour. Then about 100ml_ water was added and filtered,concentrated and the residue was extracted with ethyl acetate, purified bycolumn chromatography over silica gel (eluent : EA/PE 1/10) to afford 2,4-dibromo-1 -methyl-1 H-imidazole (20 g, yield:41 .7percent). To a solution of 2,4-dibromo-1-methyl-1 H-imidazole (6 g, 25.6 mmol) in THF (26 ml_) was added Cul (0.2 g,1mmol), Et3N (12 ml_,86 mmol),Pd(dppf)CI2 (417 mg, 0.5 mmol),Ethynyl-trimethyl-silane (4.2 ml_,29.6 mmol), then the mixture was heated to40°C and stirred at this temperature for 40min. Then filtered, concentrated andpurified by column chromatography over silica gel (eluent: EA/PE 1/50), collectthe desire fraction and concentrated to give 4-Bromo-1-methyl-2-trimethylsilanylethynyl-1 H-imidazole (3.95 g, yield: 60percent). To a solution of 4-Bromo-1-methyl-2-trimethylsilanylethynyl-1 H-imidazole (5.14 g, 20 mmol) in toluene(100 ml_) , 2-Tributylstannanyl- thiazole (8.3 g, 22 mmol) was added followedwith Pd(PPh3) (1 .2 g, 1 mmol), then themixture was refluxed for 6 hour, when cooled, the mixture was filtered, thefiltrate was concentrated and purified by chromatography over silica gel (eluent :EA/PE 1/20 to 1/10) to afford 2-(1-Methyl-2-trimethylsilanylethynyl-1 H-imidazol-4-yl)-thiazole (2.5 g, yield:48percent). To the mixture of 2-(1 -Methyl -2-trimethylsilanylethynyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-thiazole in MeOH (50 ml_), Na2CO3 (1 .5 g, 18 mmol) was added quickly and stirred the mixture forabout one minutes, then filtered, concentrated and purified by column chromatographyover silica gel (eluent: EA PE 1/5) to afford 2-(2-Ethynyl-1 -methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-thiazole (2 g, yield: 80percent). 1H NMR (CDCI3 400 MHz TMS):53.40 (s, 1 H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 7.27 (s, 1 H), 7.53 (s, 1 H), 7.26-7.27 (d, J=4.0Hz, 1 H). |
| 95 g |
With bromine; sodium acetate; acetic acid; at 20℃; for 2.5h; |
To a solution of Example 69a (82 g, 1.0 mol) and sodium acetate (125 g, 1.52 mol) in acetic acid (2.0 L) at room temperature was added bromine (480 g, 30 mmol) dropwise as a solution in 1.0L acetic acid. The resulting mixture was stirred for 2.5 h at room temperature. Acetic acid was removed in vacuo; the residue was suspended in 1.5L water and stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The resultant precipitate was filtered, washed with water and dried under high vacuum to give Example 69b (95.0 g, contained 30percent isomer) as light yellow powder. LCMS [M+H]+=319.1 |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science













 HazMat Fee +
HazMat Fee +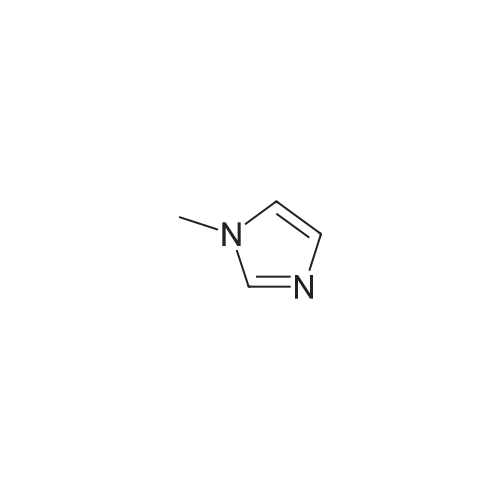

 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping