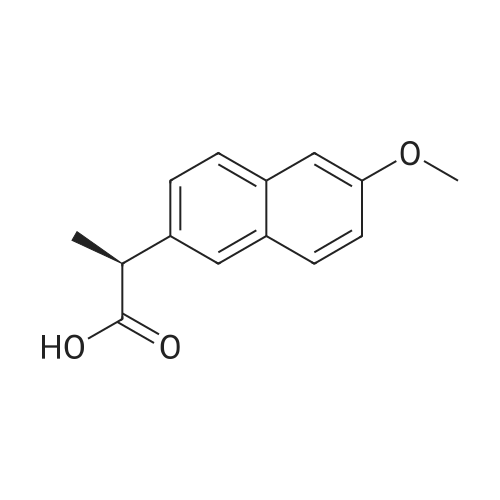
Characterization of naproxen salts with amino acid esters and their application in topical skin preparations
?wi?tek, Ewelina
;
Janus, Ewa
;
Ossowicz-Rupniewska, Paula
, et al.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.,2024,114505.
DOI:
10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114505
PubMed ID:
39306198
More
Abstract: In the study, the modification of naproxen (NAP) with esters of four amino acids (AAs): glycine (GlyOiPr), L-proline (ProOiPr), L-leucine (LeuOiPr), and L-serine (SerOiPr) isopropyl ester was performed to improve water solubility and enhance the permeation of the drug through the skin in comparison to the parent NAP. The NAP derivatives were prepared using the equimolar ratio of the components. In-depth NMR and FTIR analysis revealed that the salts formed with the proton transfer from the carboxylic group of NAP to the amine group of the appropriate AA ester. The NAP salts exhibited improved solubility in water and PBS solution (pH 7.4) when compared to parent NAP. The values of the partition coefficient (log PO/W) for prepared salts were lower than for NAP, however, the salts maintained hydrophobic character determined by the positive values of log P. The In vitro permeation through the pig skin performed in Franz diffusion cells showed that all NAP salts exhibited a higher cumulative mass of permeated NAP (Q24h) than the parent acid. The highest permeation value was noted for [ProOiPr][NAP], with a pseudo-steady state flux (Jss) 32.5?μg NAP cm?2h?1, and Q24h?=?246.4?μg NAP cm?2, it was 2.5?% of the applied dose. Moreover, topical preparations with [ProOiPr][NAP] and NAP were prepared based on two vehicles ? Celugel? and Pentravan?- approved in pharmacy recipes. The permeation experiments through the Strat-M? showed, that both the Jss and Q24h of permeated drug from preparations containing [ProOiPr][NAP], were statistically several times greater than from the respective preparations with the unmodified acid. Additionally, preparations with [ProOiPr][NAP] provided significantly improved permeation of NAP than two commercial preparations, one of which contained naproxen as the acid and the other - as the sodium salt.
Keywords:
amino acid isopropyl esters ;
naproxen ;
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ;
skin ;
permeation ;
topical compositions
Purchased from AmBeed:
22204-53-1

Targeting Glial Cells by Organic Anion-Transporting Polypeptide 1C1 (OATP1C1)-Utilizing l-Thyroxine-Derived Prodrugs
Tonduru, Arun Kumar
;
Maljaei, Seyed Hamed
;
Adla, Santosh Kumar
, et al.
J. Med. Chem.,2023,66(22):15094-15114.
DOI:
10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01026
PubMed ID:
37930268
More
Abstract: OATP1C1 (organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1C1) transports thyroid hormones, particularly thyroxine (T4), into human astrocytes. In this study, we investigated the potential of utilizing OATP1C1 to improve the delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs into glial cells. We designed and synthesized eight novel prodrugs by incorporating T4 and 3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine (DIT) as promoieties to selected anti-inflammatory drugs. The prodrug uptake in OATP1C1-expressing human U-87MG glioma cells demonstrated higher accumulation with T4 promoiety compared to those with DIT promoiety or the parent drugs themselves. In silico models of OATP1C1 suggested dynamic binding for the prodrugs, wherein the pose changed from vertical to horizontal. The predicted binding energies correlated with the transport profiles, with T4 derivatives exhibiting higher binding energies when compared to prodrugs with a DIT promoiety. Interestingly, the prodrugs also showed utilization of oatp1a4/1a5/1a6 in mouse primary astrocytes, which was further supported by docking studies and a great potential for improved brain drug delivery.
Purchased from AmBeed:
22071-15-4 ;
10236-47-2 ;
22204-53-1 ;
530-78-9 ;
5104-49-4 ;
5104-49-4 ;
22204-53-1
-Utilizing l-Thyroxine-Derived Prodrugs.png)
Cations of amino acid alkyl esters conjugated with an anion from the group of NSAIDs-As tunable pharmaceutical active ionic liquids
Klebeko, Joanna
;
Ossowicz-Rupniewska, Paula
;
Nowak, Anna
, et al.
J. Mol. Liq.,2023,384,122200.
DOI:
10.1016/j.molliq.2023.122200
More
Abstract: Herein, we investigated the effect of pairing the L-amino acid alkyl (Pr, iso-Pr, or butyl) ester on the formation of API-ILs. The novel salts of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) obtained from biodegradable cations were synthesized and characterised by NMR (NMR), Fourier transform IR spectroscopy (FT-IR), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) methods. The influence of structure counterions for APIs from the NSAIDs group on their physicochem. properties was studied in detail. The comprehensive effects of cation structure on skin permeation, accumulation, and antioxidant activity of API-ILs were also evaluated. These results demonstrated that L-amino acid alkyl esters can be successfully used to synthesize API-ILs further used in topical formulations with anti-ageing, anti-inflammatory, or photoprotective effects.
Keywords:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ;
Amino acid ester salts ;
Ionic liquids ;
Topical delivery ;
Skin barrier
Purchased from AmBeed:
15687-27-1 ;
22204-53-1

Exposure to a rotating magnetic field as a method of increasing the skin permeability of active pharmaceutical ingredients
Rakoczy, Rafal
;
Nowak, Anna
;
Konopacki, Maciej
, et al.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.,2023,185,183-189.
DOI:
10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.02.017
PubMed ID:
36905969
More
Abstract: The paper presents a method of increasing the permeability of various active substances through the skin by means of a rotating magnetic field. The study used 50 Hz RMF and various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) such as caffeine, ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen, and paracetamol. Various concentrations of active substance solutions in ethanol were used in the research, corresponding to those in com. preparations Each experiment was conducted for 24 h. It was shown that, regardless of the active compound used, an increase in drug transport through the skin was observed with RMF exposure. Furthermore, the release profiles depended on the active substance used. Exposure to a rotating magnetic field has been shown to effectively increase the permeability of an active substance through the skin.
Keywords:
Electromagnetic field ;
Rotating magnetic field ;
Active pharmaceutical ingredients ;
Transdermal drug delivery ;
Skin barrier
Purchased from AmBeed:
15687-27-1 ;
22204-53-1

Novel Naproxen Salts with Increased Skin Permeability
Swiatek, Ewelina
;
Ossowicz-Rupniewska, Paula
;
Janus, Ewa
, et al.
Pharmaceutics,2021,13(12):2110.
DOI:
10.3390/pharmaceutics13122110
PubMed ID:
34959392
More
Abstract: The paper presents the synthesis, full identification, and characterization of new salts-L-proline alkyl ester naproxenates [ProOR][NAP], where R was a chain from Et to Bu (including isopropyl). All obtained compounds were characterized by NMR (NMR), Fourier transform IR spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray powder diffractometry (XRD), and in vitro dissolution studies. The sp. rotation, phase transition temperatures (m.p.), and thermal stability were also determined In addition, their lipophilicity, permeability, and accumulation in pigskin were determined Finally, toxicity against mouse L929 fibroblast cells was tested. The obtained naproxen derivatives showed improved solubility and higher absorption of drug mols. by biol. membranes. Their lipophilicity was lower and increased with the increase in the alkyl chain of the ester. The derivative with iso-Pr ester had the best permeability through pigskin. The use of L-proline iso-Pr ester naproxenate increased the permeation of naproxen through the skin almost four-fold. It was also shown that the increase in permeability is not associated with addnl. risk: all compounds had a similar effect on cell viability as the parent naproxen.
Keywords:
amino acid ;
ionic liquids ;
naproxen ;
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ;
skin barrier ;
transdermal drug delivery
Purchased from AmBeed:
22204-53-1


 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping



-Utilizing l-Thyroxine-Derived Prodrugs.png)