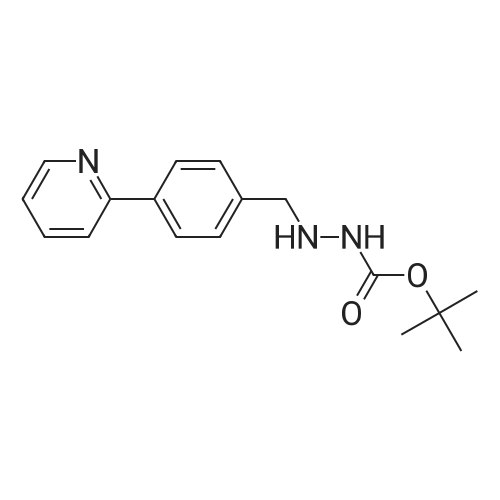
| 91% |
With sulfuric acid; In ethanol; tert-butyl methyl ether; at 20 - 30℃; for 4h; |
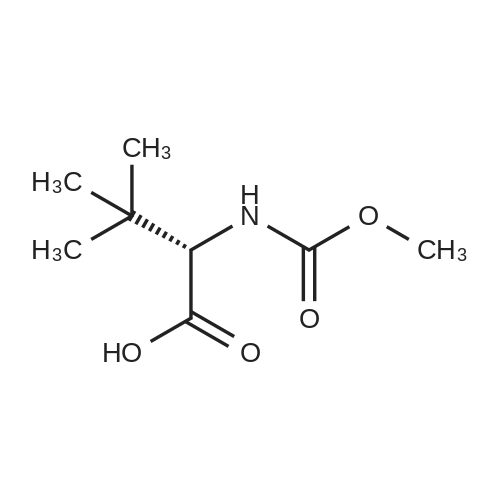
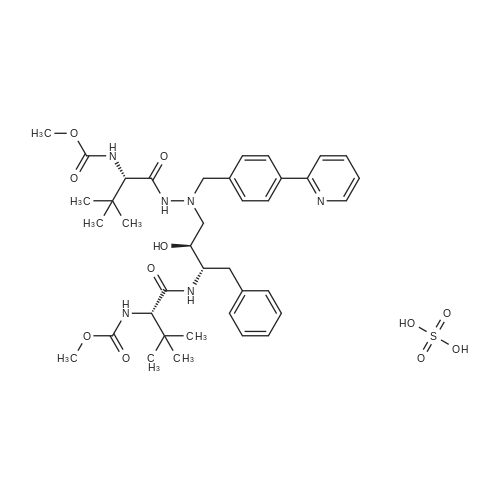
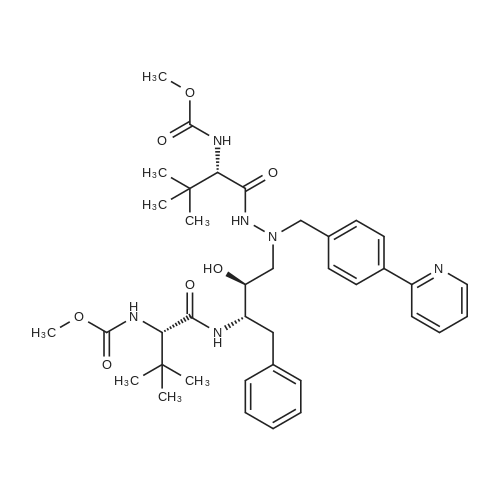
Example 3: 0.085 mL of sulfuric acid (concentrate, 1.1 equiv) was added into the mixture of 1 g of <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> base, 7.5 mL of EtOH (7.5 vol) and 7.5 mL of MTBE (7.5 vol) at 20-30 C. The resulting clear amber solution was stirred at 20-30 C. for 4 hr. The product was filtered, washed with a mixture of EtOH/MTBE (1:2, 3 mL, 3 vol), and dried under vacuum at 40-50 C. for 16 hr to afford <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> sulfate in Form A (1.04 g, 91% yield, 99.9% HPLC purity). |
| 87.8% |
With sulfuric acid; In methanol; ethyl acetate; at 43℃; for 1h; |
Example 2: Preparation of compound (A) using ethyl acetate: methanol A solvent mixture of 500 ml of ethyl acetate and 50 ml of methanol was added to 100 gms of (3S,8S,9S,12S)-3,12- bis(l ,l-dimethylethyl)-8-hydroxy-4,l l-dioxo-9-(phenylmethyl)-6-[[4-(2- pyridinyl) phenyl]methyl]-2,5,6,10,13-pentaazatetradecanedioic acid dimethyl ester [Compound (II)]. The reaction mixture was stirred at a temperature of 27±2C to get a suspension. The temperature of the suspension was then raised to 43±2C and 7.5 ml (13.9 gms) of sulphuric acid was added slowly. The solution was maintained for an hour at a temperature of 43±2C whereby a solid was obtained. The material was cooled down to a temperature of 27±2C. To this 200 ml of ethyl acetate was added, followed by chilling the reaction mixture at a temperature of 3±2C. The solid obtained was filtered and washed with 1 volume of ethyl acetate. The solid was then exposed to drying process under vacuum at 27±2C for 2 hours. The material was powdered and again exposed to drying process under vacuum (630±20 mm of Hg) at 53±2C for 4 hours. The drying process was continued till the LOD (loss on drying) was less than 0.5%w/w to obtain the title compound. Dry weight: lOOgms Yield: 87.8% HPLC Purity: 99. 9% |
| 74.3% |
With potassium fluoride; sulfuric acid; In ethanol; n-heptane; at 15 - 37℃; for 8.25h; |
EXAMPLE 3 <strong>[198904-31-3]Atazanavir</strong> Bisulfate-Form E3 (Triethanol Solvate) <strong>[198904-31-3]Atazanavir</strong> free base (prepared as described in Example 1, Part C) (3.0 g, 4.26 mmol) was slurried in dry, 200 proof ethanol (20.25 mL, 6.75 mL/g of free base) in a 100 mL, 3-neck round-bottom flask fitted with a mechanical stirrer, temperature probe, and a pressure-equalizing liquid addition funnel. Concentrated H2SO4 (0.25 mL, 0.46 g, 4.69 mmol, 1.1 eq.) was added to the slurry of <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> free base which was maintained at 20-25 C. The resulting solution (KF of 0.2 to 1.0% water) was polish filtered (Whatman #1 paper), the filter rinsed with 2.25 mL of absolute ethanol and the rinse added to the filtered solution. The solution was heated to 37 C. and seeded with 10 mg of amorphous <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> bisulfate derived from Form E3 crystals (by exposing Form E3 crystals to ambient temperature), and the mixture was agitated for 15 min. Heptane (380 mL, 8.25 mL/g of free base) was added over 1 hour. The resulting crystallization mixture was agitated for 8 h at 15-25 C. Crystallized <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> bisulfate was filtered on a Buchner funnel. The product cake was washed with 184 mL (4 mL/g of free base) of 1:1 ethanol: heptane. The product cake was washed with 46 mL (1 mL/g of free base) of heptane. The resulting product was dried under vacuum at 40-50 C. until it had an LOD=0.97%. The yield of product was 47.7 g (0.0594 mol, 74.3 mol %) of <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> bisulfate Form E3 (triethanol solvate) with HPLC HI=100.0 (see FIGS. 9 and 10). |
|
With sulfuric acid; In 1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one; acetone; at 20 - 50℃; for 7h; |
E. 1-[4-(Pyridin-2-yl)phenyl]-5(S)-2,5-bis [N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucinyl]amino}-4(S)-hydroxy-6-phenyl-2-azahexane bisulfate salt About 10% (2 g) of the total charge of concentrated sulfuric acid (19 g, 1.10 eq.) was added to the free base acetone/N-methylpyrrolidone solution of Part D, while maintaining the temperature at 40-50 C., via subsurface addition. The reaction mixture was seeded with 5.0 wt % (wrt calculated free base in solution) of bisulfate salt. The seeded mixture was agitated at 40-50 C. for at least 30 minutes during which time the bisulfate salt began crystallizing as evidenced by the mixture increasing in opacity during this time. The remaining sulfuric acid (17.8 g) was added over ca. 5 h in five stages according to the following protocol, defined by a cubic equation, while keeping the temperature at 40-50 C. The rate of each addition stage was determined according to the cubic equation described hereinbefore and is shown in the table below. TABLE 1 Stage mL/kg/h mL(H2SO4)/h g(H2SO4)/h Duration (min) 1 4.62 0.579 1.065 60 2 6.93 0.868 1.597 60 3 16.55 2.073 3.814 60 4 30.26 3.790 6.974 60 5 48.47 6.071 11.171 23 After addition of H2SO4 was complete, the slurry was cooled to 20-25 C. for at least 1 h with agitation. The slurry was agitated at 20-25 C. for at least 1 h. The bisulfate salt was filtered and the mother liquor was recycled as needed to effect complete transfer. The filter cake was washed with acetone (5-10 mL/g of free base; 1200 mL acetone). The bisulfate salt was dried at NMT 55 C. under vacuum until the LOD<1% to produce a crystalline material. The crystalline product was analyzed by PXRD, DSC and TGA patterns and SSNMR spectrum and found to be (non-solvated) Form A crystals of the title bisulfate (see FIGS. 1 to 5). |
|
With sulfuric acid; In ethanol; at 25 - 30℃; for 0.666667h;Industry scale; |
To a solution of <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> base (60 Kg) in ethanol (390 L), concentrated sulfuric acid (5.16 L) was added at 25 - 30C and stirred for 40 minutes. To the solution n-heptane (498 L) and seed of <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> sulfate ( 80 g) were added. Stirred at 25 - 30C for 16 hours. The solid was filtered, washed with 1 : 1 mixture of ethanol: n-heptane and dried to give 58 Kg of <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> sulfate. (HPLC data: <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> sulfate - 99.93%, RSSS isomer - 0.01%, SSSR isomer - 0,01 %, RSSR isomer - below detection limit). |
|
With sulfuric acid; In acetone; at 40 - 45℃; |
Example 7: Preparation of <strong>[198904-31-3]Atazanavir</strong> Bisulfate (1 : 1) Formula I To <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> (150 g; obtained in Example 6), dichloromethane (900 mL) and N- methylpyrrolidine (188 mL) were added under stirring at ambient temperature and further stirred for 30 minutes to 40 minutes. After the solution became clear, activated carbon (7.5 g) was added and further stirred for 30 minutes to 40 minutes at ambient temperature. The reaction mixture was filtered through a hyflo-bed and the bed was washed twice with dichloromethane (2 x 150 mL). The filtrates were combined, heated to 40C to 45C and dichloromethane was recovered atmospherically. Sequentially, acetone (2 x 750 mL) was added to the reaction mass, the solution so obtained was heated to 60C to 65C and acetone was recovered atmospherically and then vacuum was applied for 30 minutes to 45 minutes at 60C to 65C. After that, acetone (2400 mL) was added at the same temperature and then cooled to 40C to 45C. Concentrated sulfuric acid (22.96 g) was slowly added over a period of 3 hours to 4 hours at 40C to 45C and stirred for 30 minutes to 40 minutes. The reaction mixture was cooled to 20C to 25C and stirred for 3 hours to 4 hours at 20C to 25C. The solid was filtered and acetone (1200 mL) was added at 20C to 25C to the wet cake and stirred for 15 minutes to 20 minutes. The solid was filtered, washed with acetone (150 mL) and dried under vacuum at 45C to 50C to afford the title compound. Yield(w/w): 1.03 |
|
|
Example 7 Preparation of <strong>[198904-31-3]Atazanavir</strong> Bisulfate (1:1) To <strong>[198904-31-3]atazanavir</strong> (150 g; obtained in Example 6), dichloromethane (900 mL) and N-methylpyrrolidine (188 mL) were added under stirring at ambient temperature and further stirred for 30 minutes to 40 minutes. After the solution became clear, activated carbon (7.5 g) was added and further stirred for 30 minutes to 40 minutes at ambient temperature. The reaction mixture was filtered through a hyflo-bed and the bed was washed twice with dichloromethane (2*150 mL). The filtrates were combined, heated to 40 C. to 45 C. and dichloromethane was recovered atmospherically. Sequentially, acetone (2*750 mL) was added to the reaction mass, the solution so obtained was heated to 60 C. to 65 C. and acetone was recovered atmospherically and then vacuum was applied for 30 minutes to 45 minutes at 60 C. to 65 C. After that, acetone (2400 mL) was added at the same temperature and then cooled to 40 C. to 45 C. Concentrated sulfuric acid (22.96 g) was slowly added over a period of 3 hours to 4 hours at 40 C. to 45 C. and stirred for 30 minutes to 40 minutes. The reaction mixture was cooled to 20 C. to 25 C. and stirred for 3 hours to 4 hours at 20 C. to 25 C. The solid was filtered and acetone (1200 mL) was added at 20 C. to 25 C. to the wet cake and stirred for 15 minutes to 20 minutes. The solid was filtered, washed with acetone (150 mL) and dried under vacuum at 45 C. to 50 C. to afford the title compound. |
|
With sulfuric acid; In 1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one; acetone; at 40 - 50℃; for 0.5h; |
About 10% (2 g) of the total charge of concentrated sulfuric acid (19 g, 1.10 eq.) is added to the free base acetoneN-methylpyrrolidone solution of Part D, while maintaining the temperature at 40-50 C., via subsurface addition. The reaction mixture is seeded with 5.0 wt % (wrt calculated free base in solution) of sulfate salt. The seeded mixture is agitated at 40-50 C. for at least 30 minutes during which time the sulfate salt began crystallizing as evidenced by the mixture increasing in opacity during this time. The remaining sulfuric acid (17.8 g) is added over ca. 5 h in five stages according to the following protocol, defined by a cubic equation, while keeping the temperature at 40-50 C. The rate of each addition stage is determined according to the cubic equation described in U.S. Patent Publication No. U520050256202A1, published Nov. 17, 2005. After addition of H2504 is complete, the slurry is cooled to 20-25 C. for at least 1 h with agitation. The slurry is agitated at 20-25 C. for at least 1 h. The sulfate salt is filtered and the mother liquor is recycled as needed to effect complete transfet The filter cake is washed with acetone (5-10 mEg of free base; 1200 mE acetone). The sulfate salt is dried at NMT 55 C. under vacuum until the LOD<1% to produce a crystalline material. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping