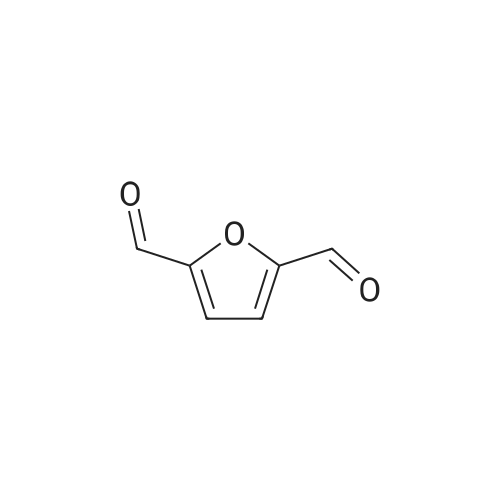
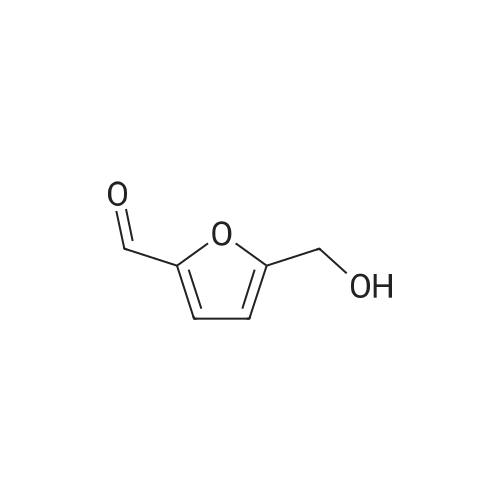
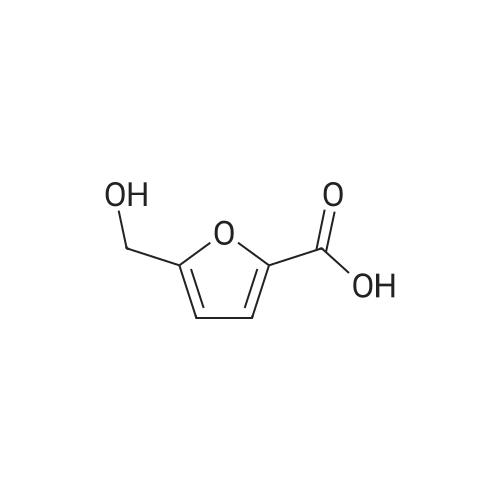
|
With sodium hydroxide; 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide; at 0 - 20℃; |
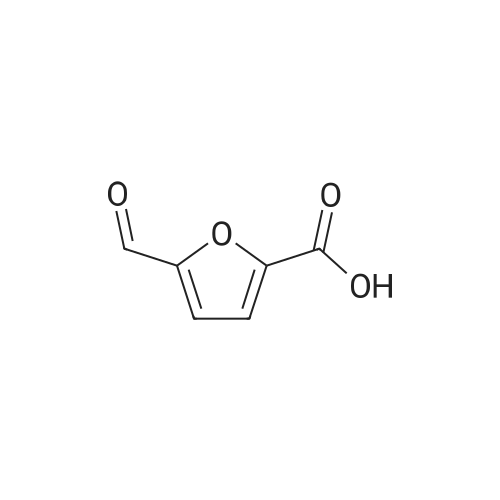
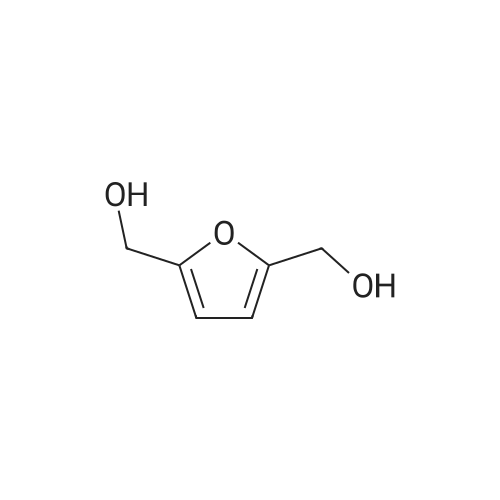
With reference to Scheme 1 below, 1 ml of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([EMIm]TFSI, available from Merck) newly serving as an ionic liquid was placed in a round-bottom flask, 0.126 g (1 mmol) of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF, Compound I) was dissolved, the reaction temperature was adjusted to 0° C., and then sodium hydroxide powder (0.200 g, 5 mmol) was added thereto. Subsequently, the reaction temperature was increased to room temperature so that the reaction took place. After completion of the reaction, 20 ml of dichloromethane was added, after which the filtrate obtained via filtration, namely, the dichloromethane layer was distilled under reduced pressure, thus recovering the ionic liquid. [0057] The lump of filtered particles resulting from recovering the ionic liquid was dissolved in 2 ml of water, and then neutralized with 1 N HCl, so that the pH of the solution was adjusted to about 78. Extraction using ethyl acetate (3×50 ml) and then concentration under reduced pressure were conducted, yielding 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran (DHMF, Compound II) as a white solid. [0058] The pH of the remaining water layer was adjusted to about 3, followed by performing extraction using ethyl acetate and then concentration under reduced pressure, yielding 5-hydroxymethylfuranoic acid (HMFA, Compound III) as a light yellow solid. The yields of the products are shown in Table 1 below. [0059] The melting point of the light yellow crystals was 239.5° C., and the light yellow crystals were analyzed to be a target compound using 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR. The analytic data was as follows. [0060] HMFA: 1H NMR (300 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 7.16 (d, J=3.4, 1H), 6.47 (d, J=3.4, 1H), 4.59 (s, 2H) ; 13C NMR (75 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 160.9, 159.5, 144.9, 119.6, 109.6, 57.3. [0061] DHMF: 1H NMR (300 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 6.18 (s, 2H), 4.48 (d, J=5.8, 4H), 4.18 (t, J=5.8, 2H) ; 13C NMR (75 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 155.8, 108.22, 57.2. |
|
With 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate; sodium hydroxide; at 0 - 20℃; |
DHMF and HMFA were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, with the exception that 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([BMIm]BF4, available from C-TRI) was used as the ionic liquid instead of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([EMIm]TFSI). [0075] The melting point of the light yellow crystals was 239.5° C., and the light yellow crystals were analyzed to be the target compound using 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR. The analytic data was as follows. [0076] HMFA: 1H NMR (300 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 7.16 (d, J=3.4, 1H), 6.47 (d, J=3.4, 1H), 4.59 (s, 2H) ; 13C NMR (75 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 160.9, 159.5, 144.9, 119.6, 109.6, 57.3. [0077] DHMF: 1H NMR (300 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 6.18 (s, 2H), 4.48 (d, J=5.8, 4H), 4.18 (t, J=5.8, 2H) ; 13C NMR (75 MHz, acetone-d6): delta 155.8, 108.22, 57.2. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping