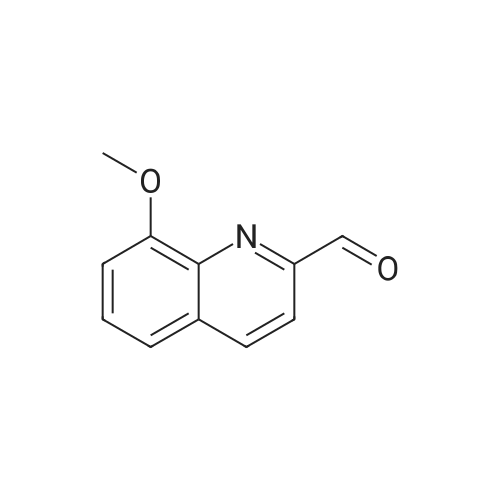
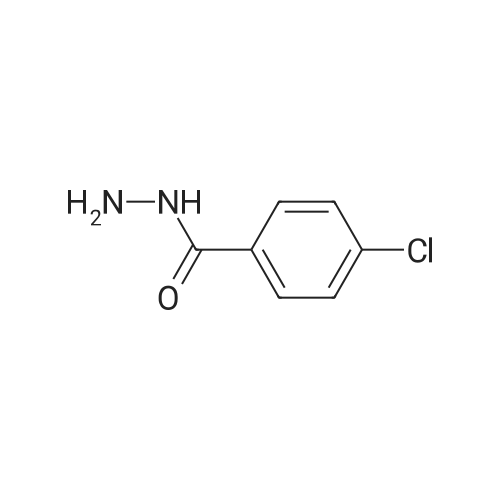
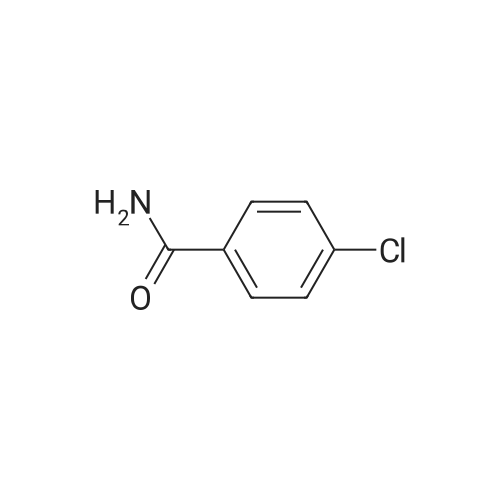
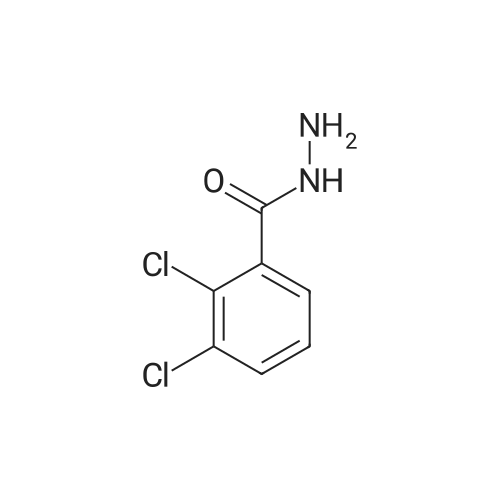
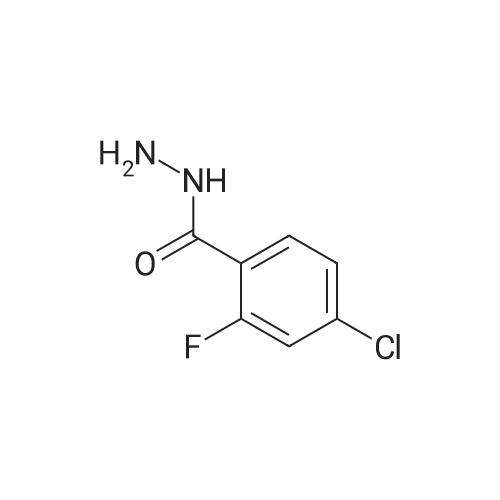
|
With hydrazine hydrate; In methanol; for 8h;Reflux; |
General procedure: To a solution of methyl ester of aromatic carboxylic acid 2 (0.1 mol) in methanol (30 mL), hydrazine hydrate (0.2 mol) was added drop wise with stirring. The resulting mixture was allowed to reflux for 8 h. After the completion of the reaction as monitored by TLC, the excess methanol was distilled off under reduced pressure. The resulting acid hydrazide 3 was washed with cold water, dried and recrystallized from ethanol. |
|
With hydrazine hydrate;Reflux; |
General procedure: One millimole of the corresponding ester was added insmall portion to a round bottom flask containing solution ofhydrazine hydrate (10 ml) and followed by stirring themixture under reflux conditions. When completion of thereaction was monitored by TLC, the media was poured ontoice bath and the resulting precipitation was isolated by filtration.The corresponding acid hydrazide was afforded andrecrystallized from ethanol and water. |
|
With hydrazine hydrate; In methanol; at 65℃; for 4h; |
General procedure: To a solution of esters (2a~2t, 1.0 equiv.), furan-2-carbonyl chloride (7a, 1.0 equiv.) orthiophene-2-carbonyl chloride (7b, 1.0 equiv.) in MeOH (2 mL/1 mmol) was added hydrazine hydrate(1 mL/1 mmol), then the mixture was allowed to reach 65 C and stirred for 4 h. After completion(monitored by TLC), the organic solvent was removed and extracted three times with ethyl acetate,the combined organic extracts were dried (Na2SO4) and concentrated under reduced pressure to givethe corresponding hydrazides (3a~3t, 8a, or 8b) in high yields, which were taken up for the next stepwithout any purification. |
|
With hydrazine hydrate; In methanol;Reflux; Inert atmosphere; |
General procedure: Hydrazine hydrate (5 mL, 40%) was added to a solution of requiredester (5.0 mmol) in methanol (20 mL). The solution was refluxed for12-24 h and monitored by TLC until starting material was completelyconsumed. After that, solvent was evaporated under reduced pressureand a small amount of water (5 mL) was added to precipitate the hydrazide,which was filtered and dried in vacuum to give a shiny white toyellow solid in excellent yields, without further purification. |
|
With hydrazine hydrate; In methanol; at 80℃; for 4h; |
General procedure: At the 250 cm3double-mouth bottle, 13.5 mmol of themethyl benzoate derivatives was added to 100 cm3of methanol,added 6.75 cm3of hydrazine hydrate (108 mmol) tothe reaction mixture slowly. After that warming to 80 Cand reflux for 4 h until the reaction was completed, thenconcentrated under reducing pressure to remove methanol,filtering and drying to get white solid 2. |
|
With hydrazine hydrate; In ethanol;Reflux; |
General procedure: Method A Methyl benzoate derivatives (2, 1 eq) and 85% hydrazine hydrate (10 eq) were dissolved in ethanol (45 mL). The mixture was refluxed overnight. After cooling, the solvent was removed in vacuo and the residue was separated on the Biotage SNAP Cartridge KP-Sil 100 g eluting with 0-60 % ethyl acetate/petroleum ether to afford compound 4. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping