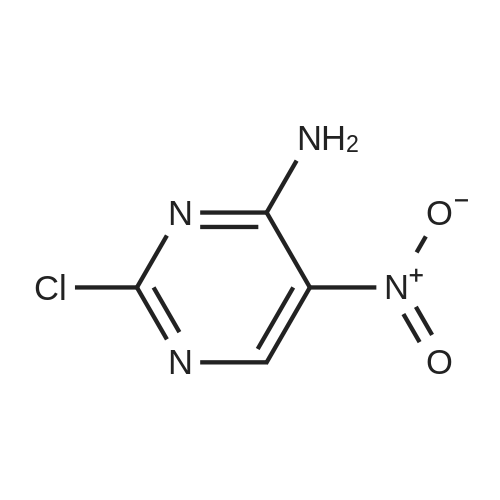
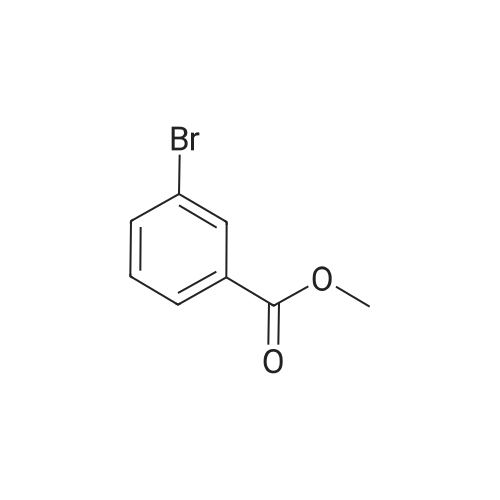
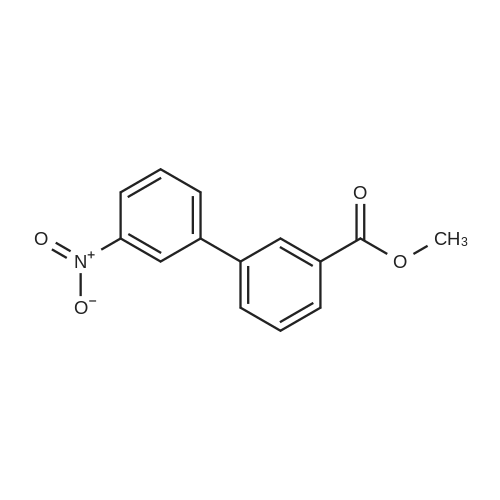
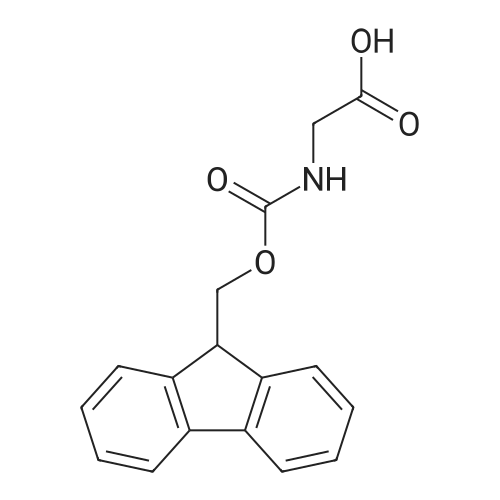
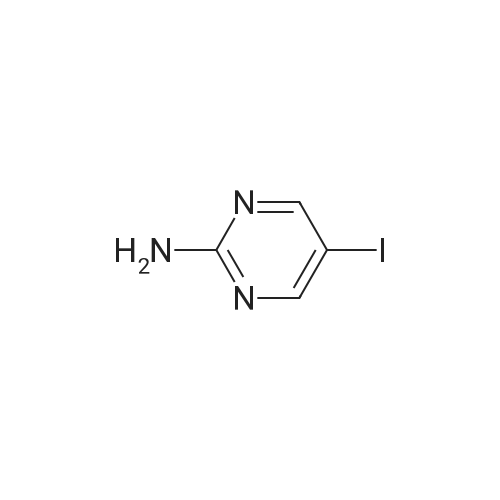
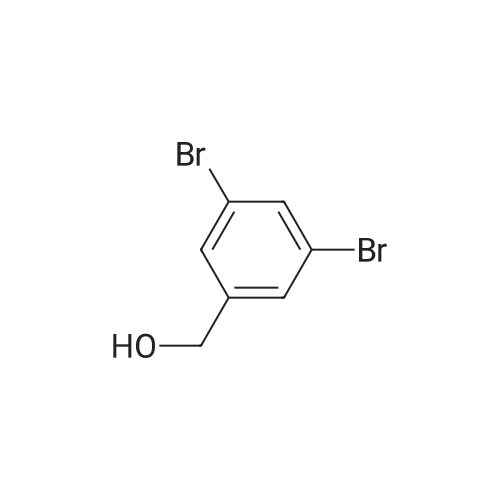
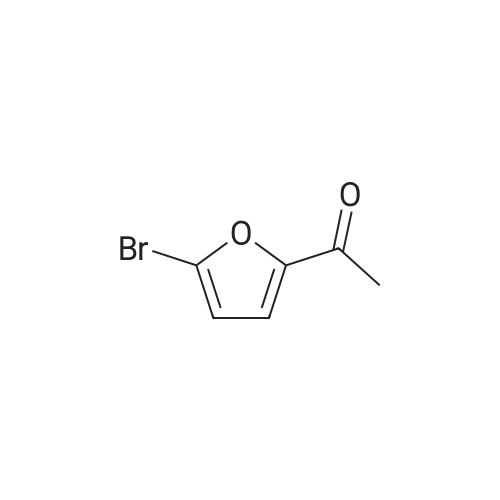
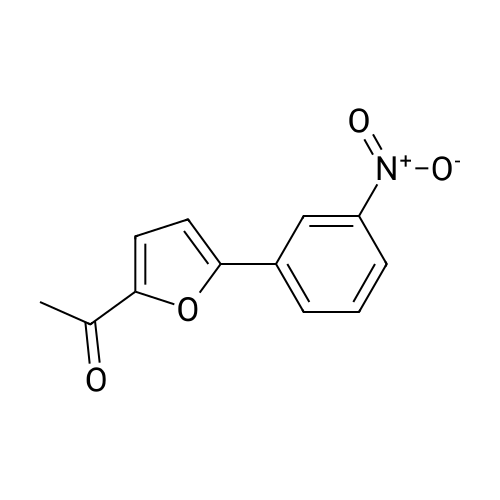
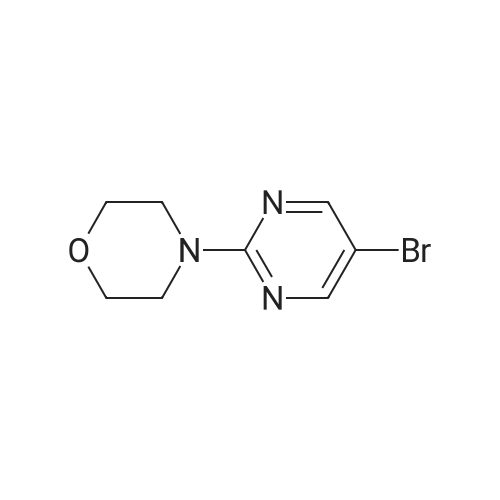
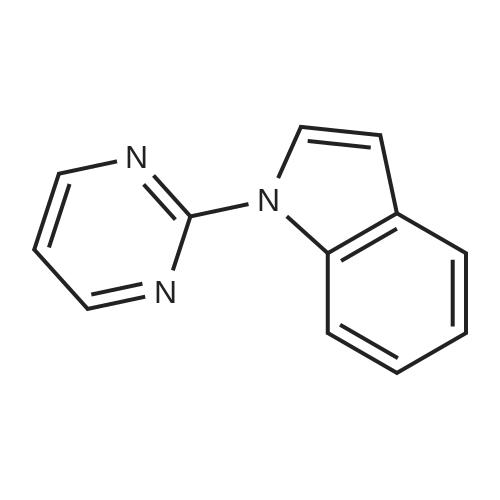
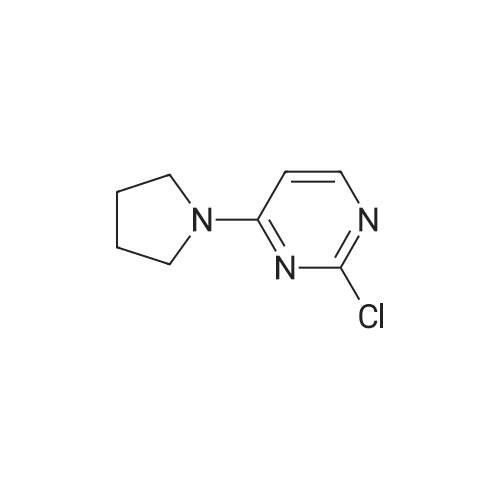
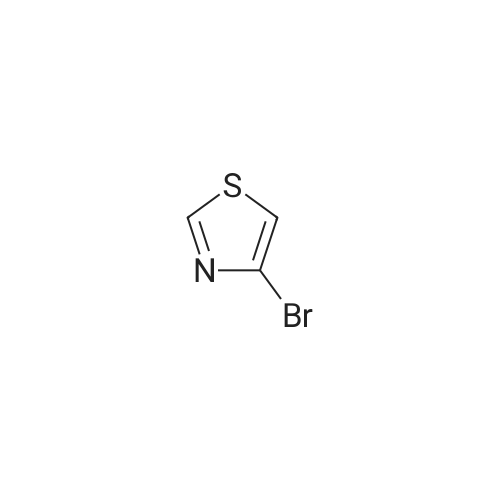
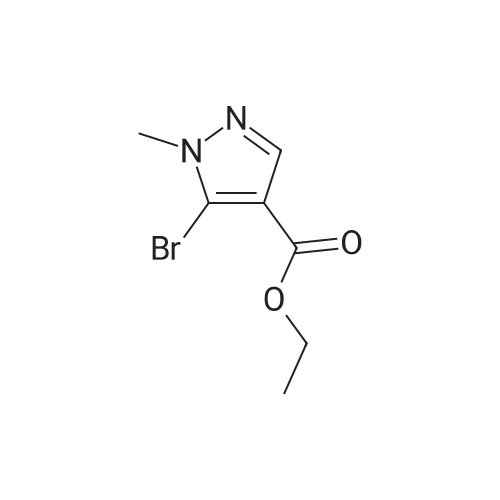
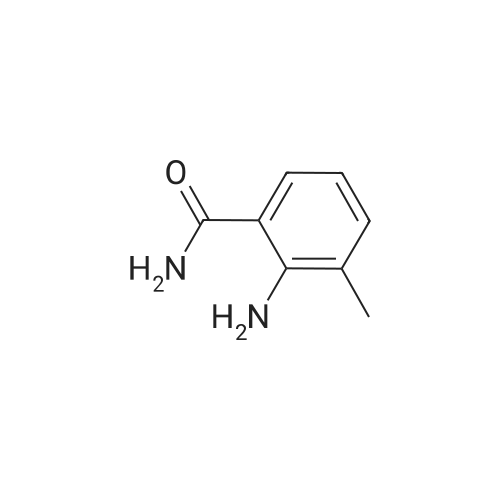
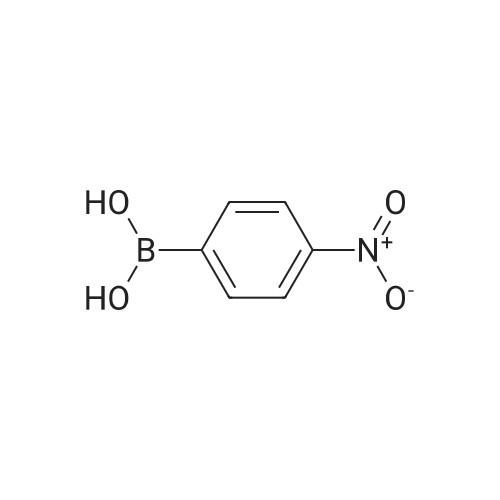
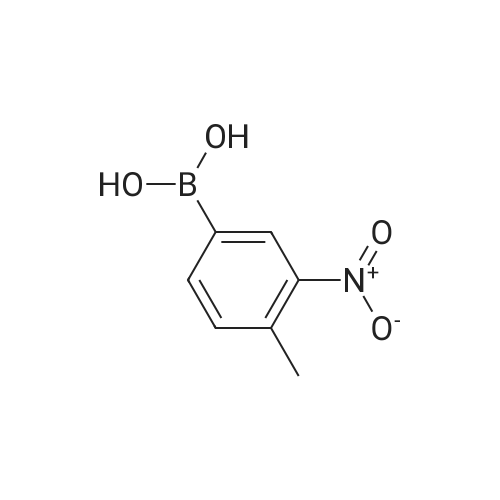
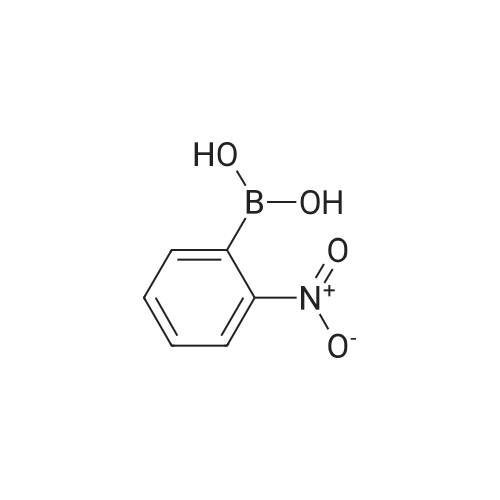
| 93% |
With Pd/C; potassium carbonate; In water; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; at 110℃; for 2.5h; |
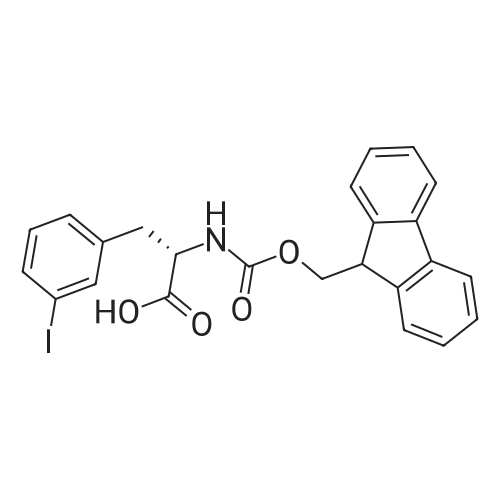
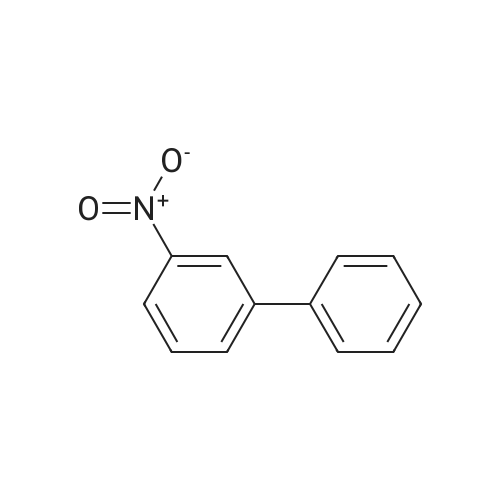
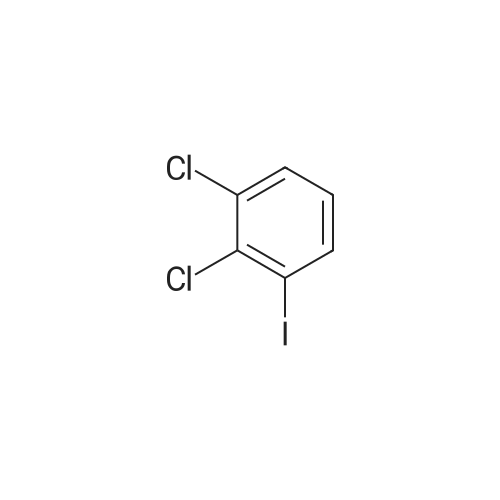
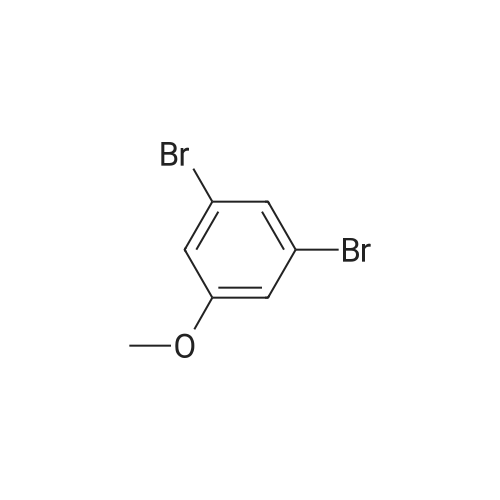
General procedure: To a tube equipped with a magnetic stir bar were added catalyst 1(7.0 mg, 0.1 mol% Pd), K2CO3 (138 mg, 2.0 equiv), arylboronicacid (1.1 equiv), and aryl bromide (0.5 mmol) in turn. Subsequently,the solvent (DMF-H2O, 3:2, 2.0 mL, v/v) was added under an airatmosphere. The reaction was then heated to 40 C and stirred untilthe aryl bromide was completely consumed as determined by TLC.After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was purifiedby silica gel column chromatography to afford the desired pureproduct. |
| 90% |
With potassium carbonate; In water; at 50℃; for 3h; |
General procedure: In a test tube equipped with a magnetic stirrer bar, thearyl halide 1 (1 mmol) was mixed with phenyl boricacid 2 (1.2 mmol), K2CO3(2 mmol), and the Pd-catalyst(0.1mol% Pd) in 2 ml of H2Oin air. The reaction mixturewas then stirred at 50 C for appropriate time. After completionof the reaction, the catalyst was removed by magnetand washed with ethanol and water (3 × 5 ml). The aqueouslayer was extracted with chloroform, then organic layerdried over anhydrous MgSO4.The solvent was evaporatedunder reduced pressure to give the corresponding biarylcompounds. All the products were previously reported [5,8-12] and were confirmed by the spectroscopic methodusing 1H and 13C NMR (see supporting information). |
| 87% |
With 0.1 % Cu/C; potassium carbonate; In water; at 50℃; for 4h;Green chemistry; |
General procedure: In a test tube, 1.0 mmol of aryl halides 1, 1.2 mmol of phenylboronic acid 2 were mixed together and then 2.0 mmol of K2CO3, and the Cu/Cnano-catalyst (0.1 mol % Cu) in 2 mL of H2O, were added in air. The reaction mixture was then stirred at 50 C for appropriate time. After completion of the reaction (monitored by TLC), the catalyst was removed by simple filtration. The recycled catalyst was was hed with ethanol and water (3 × 5 mL) and dried at 60 C in oven for further use. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate, and organic layer dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give the corresponding biaryl compounds. |
| 71% |
With tetrabutylammomium bromide; potassium carbonate; In water; at 90℃; for 4h;Green chemistry; |
General procedure: 25-ml RB was charged with 4-iodo anisole (1.0 mmol), phenyl boronic acid (1.5 mmol), GO-PMMA-Pd catalyst (0.3 mol %), K2CO3 (1 mmol), TBAB (10 mol %) and 2 ml water. The mixture was allowed to stir at 90 C for an appropriate time (Table 1) and the extent of the reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC). After the completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was extracted by ethyl acetate (2×25 mL) and washed with water repeatedly. The catalyst was filtered off and washed several times with ether and water (1:1) until no significant product was obtained in the wash. The recoverd catalyst was reused for the next coupling experiment. The reaction mixture was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, concentrated in vacuum and purified by column chromatography on silica gel 60-120 mesh using petroleum ether as eluent to obtain pure product. The catalyst recoverd after 5th run was subjected to ICP-AES for Pd content analysis. The isolated products were analysed by 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopy. |
| 53% |
With Pd(memantine)2Cl2; sodium hydroxide; In ethanol; at 80℃; for 24h; |
General procedure: In the reaction tube with a magnetic bar was added the solution of aryl bromides (0.5 mmol) and phenylboronic acid (91 mg, 0.75 mmol), NaOH (24 mg, 0.6 mmol), complex 1 (0.0001-0.02 mol%, dissolved in DMA) and ethanol (3 mL). After stirred for the required time in the preset conditions, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then quenched by 1 mL brine and 3 mL water, and extracted with ethyl acetate (3×5 mL). The combined organic layer was dried over anhydrous MgSO4 and the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure. The crude products were purified by column chromatography (petroleum ether, ethyl acetate) on silica gel. |
|
With C24H20Cl2NPPdS; potassium carbonate; palladium; In toluene; at 100℃; for 24h; |
General procedure: A 100 ml round bottom flask was fitted with a reflux condenser and a magnetic stirrer bar. The flask was charged with toluene (15 ml) and the appropriate amount of catalyst reagents and the internal standard (n-Decane: 2.59 mmol). The contents were thoroughly mixed and an initial sample (t0) was then taken. The reaction flask was placed in an oil bath at the desired temperature and the reaction mixture allowed to heat/reflux with stirring. A sample was taken and analyzed every 10 min for the first hour and every 30 min thereafter until t3h. In cases where conversionwas not complete after 3 h, the reaction mixturewas then allowed to stir for a total of 24 h. The reaction at 140 C was performed in a sealed tube. All catalytic reactions were done under aerobic conditions. Percentage conversions were determined by GC with n-decane as the internal standard and the coupling products were characterized by mass spectrometry (Table 4) as well as 1H NMR spectroscopy (Entry 5, Table 4 only). |
|
With C31H33Cl2N2PPd; potassium hydroxide; In decane; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; at 150℃; for 3h;Catalytic behavior; |
General procedure: The Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions were performed in acarousel using 24 × 150 mm quick-thread glass reaction tubes. Thegeneral procedure is similar to that given for the Mizoro-Heck Crosscouplingreactions, however, boronic acid is used herein instead of analkene. The GC was initially calibrated using standard samples ofboronic acid, toluene, n-decane and the aryl halide in order to accuratelydetermine the retention times of these compounds. Also, the reactionmixture in the reaction vessel was sampled to determine time zerovalues and analysed by GC to determine the ratios of the various components.The required catalyst amount (mol %) was then added and thereaction proceeded with a stirring rate of 600 rpm. Upon the elapse ofthe reaction time, the aryl halide conversion to biphenyl was calculatedby analysing the retention peak areas of the aryl halide with reference ton-decane as an internal standard. The NMR data of the isolated productsare given in the Supplementary Information (SI2). |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping