| Acridine Basic information |
| Product Name: |
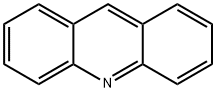
Acridine |
| Synonyms: |
10-Azaanthracene;2,3,5,6-dibenzopyridine;2,3-Benzoquinoline;9-Azaanthracene;Aceridine;Acridine;Dibenzo[b,e]pyridine;ACRIDINE, FOR FLUORESCENCE;ACRIDINE 97% |
| CAS: |
260-94-6 |
| MF: |
C13H9N |
| MW: |
179.22 |
| EINECS: |
205-971-6 |
| Product Categories: |
Highly Purified Reagents;Other Categories;Zone Refined Products;AlphabeticalBiochemicals and Reagents;Fluorescent Stains;Luminescent Compounds/Detection;Nucleic Acid Stains;Stains and Dyes;A;Stains&Dyes, A to;Aromatics;Heterocycles;Intermediates & Fine Chemicals;Metabolites & Impurities;Pharmaceuticals;Aromatics, Heterocycles, Metabolites & Impurities, Pharmaceuticals, Intermediates & Fine Chemicals;Acridine;Fluorescent |
| Mol File: |
260-94-6.mol |
 |
| |
| Acridine Chemical Properties |
| Melting point |
106-109 °C |
| Boiling point |
346 °C(lit.) |
| density |
1,005 g/cm3 |
| Fp |
346°C |
| storage temp. |
Refrigerator |
| solubility |
dioxane: 0.1 g/mL, clear |
| pka |
5.58(at 20℃) |
| form |
Crystalline Powder |
| color |
Yellow to yellow-brown |
| PH Range |
Green B uorescence (5.2) to violet B uorescence (6.6) |
| λmax |
358nm, 392nm |
| Merck |
14,122 |
| BRN |
120200 |
| Stability: |
Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Major Application |
Organic light-emitting diode, photoresists, nanosensors, fuel cells, memory device, semiconductors, information storage device, liquid crystal displays, identification of product forgeries, inks, adhesives, textile, hair dyes, gene detection assay, staining cells, biosensors, detecting nucleic acids, proteins, antiHCV antibodies, antibacterial, antiamyloid agents, wound dressing materials, vaccines against infection, allergy and cancer |
| CAS DataBase Reference |
260-94-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Hazard Codes |
Xn |
| Risk Statements |
22-68-36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements |
22-36-45-36/37/39-26 |
| RIDADR |
UN 2713 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany |
3 |
| RTECS |
AR7175000 |
| TSCA |
Yes |
| HazardClass |
6.1 |
| PackingGroup |
III |
| Provider |
Language |
| ACROS |
English |
| SigmaAldrich |
English |
| ALFA |
English |
| |
| Acridine Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties |
colourless to light yellow crystals |
| Uses |
A quinoline derivative used as manufacturing dyes and as intermediate for antileishmanial agents. A catabolic product of carbamazepine (C175840) metabolite. |
| Definition |
ChEBI: A polycyclic heteroarene that is anthracene in which one of the central CH groups is replaced by a nitrogen atom. |
| Uses |
manufacture of dyes and intermediates; some dyes derived from it are used as antiseptics, e.g. 9-aminoacridine, acriflavine and proflavine. The hydrochloride has been used as reagent for cobalt, iron and zinc. |
| General Description |
Small colorless needle-like crystalline solid. Slightly soluble in hot water. Slightly denser than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Sublimes before melting when heated. May be toxic by ingestion. |
| Air & Water Reactions |
Slightly soluble in hot water. |
| Reactivity Profile |
Acridine neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. Burns to give toxic oxides of nitrogen. |
| Health Hazard |
Inhalation irritates respiratory system and causes sneezing, crying, and vomiting. Contact with liquid irritates eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. At high temperature and during sun exposure, damage to the cornea, skin, and mucous membranes may occur following the liberation of Acridine vapor. |
| Toxicity |
LD50 s.c. in mice: 0.40 g/kg (Rubbo) |
|





 China
China