| | 198904-31-3 Basic information More.. |
| Product Name: | Atazanavir | | Synonyms: | atazanvir;Atazanavir, >=99%;Atazanavir Enantiomer;Atazanavir Isomer Impurity;Atazanavir Isomer Impurity 1;Atazanavir Isomer Impurity 2;Atazanavir Isomer Impurity 3;Atazanavir Intermediate Impurity 1 | | CAS: | 198904-31-3 | | MF: | C38H52N6O7 | | MW: | 704.86 | | EINECS: | 812-543-8 | | Mol File: | 198904-31-3.mol | 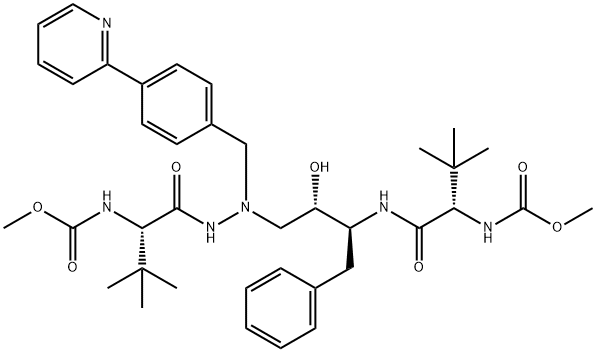 |
Use
Atazanavir is an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) protease, an
enzyme that is essential for the processing of Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins into structural
and enzymatic proteins required for viral replication. It has a similar pharmacophore motif
to the other six widely marketed HIV protease inhibitors, most of which are based upon a
hydroxyethylamine template. Uniquely, it possesses an aza-peptide motif but maintains
many similar pharmacophore elements including lipophilic moieties that presumably bind
to S2, S1, S′1
, and S′2
positions. Atazanavir is pseudo-symmetric about the central template,
incorporating D-tert-Leucine at both termini. This compound is synthesized in about seven
steps, with a key coupling of the chiral epoxide (derived from phenylalanine and imparting
one chiral center) and N-tert-boc-N′-(4-[2-pyridyl]benzyl)hydrazine. Removal of both
tert-Boc groups and double acylation with methoxycarbonyl-tert-Leucine provides the
product. Another synthesis of atazanavir entails ten steps and utilizes α-(tert-bocamino)
phenylpropanal as a chiral intermediate. It is a potent inhibitor of indinavir-resistant
and saquinavir-resistant strains of HIV-1 (IC50=0.03–0.1 and 0.04–0.1 μM,
respectively). In 300 patients who had failed previous treatment, atazanavir (400 mg
once daily) was compared to lopinavir (400 mg twice daily) and ritonavir (100 mg); both
arms additionally receiving two non-reverse transcriptase inhibitors. After 24 weeks, HIV
RNA levels of <400 copies/mL were noted in 61% of patients receiving atazanavir and
81% of those taking lopinavir/ritonavir. After 96 weeks of therapy with atazanavir, HIV
RNA copy levels were found to be <400 and <50 in 80 and 58% of patients, respectively.
A study of the cross-resistance profile relative to other protease inhibitors using a panel of
551 clinical isolates (without prior atazanavir exposure but with cross-resistance to one or
two other protease inhibitors; the majority had resistance to nelfinavir) showed that greater
than 80% retained susceptibility to atazanavir. All of the resistant isolates from patients
taking atazanavir had an I50 L substitution. The recommended dosage of atazanavir is
400 mg once daily. It has a mean half-life range of 7.9–6.5 h with about 60%
bioavailability and moderate plasma protein binding (86% albumin and 89% alpha-1-
acid glycoprotein (AAG)). Atazanavir was well tolerated in clinical studies and it
displayed minimal lipid modulation when tested in combination with two non-reverse
transcriptase inhibitors. Atazanavir had no effect on total cholesterol, low-density
lipoprotein, and triglyceride levels when compared with other protease inhibitors that
caused sustained elevations in these lipid levels.
- Atazanavir
-

- US $0.00-0.00 / KG
- 2025-04-15
- CAS:198904-31-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- Atazanavir
-

- US $0.00 / Kg/Bag
- 2025-04-11
- CAS:198904-31-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%min
- Supply Ability: 100KGS
- Atazanavir
-

- US $0.00 / KG
- 2025-03-21
- CAS:198904-31-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month
|
|
198904-31-3
Recommend Suppliers |
|