68414-18-6
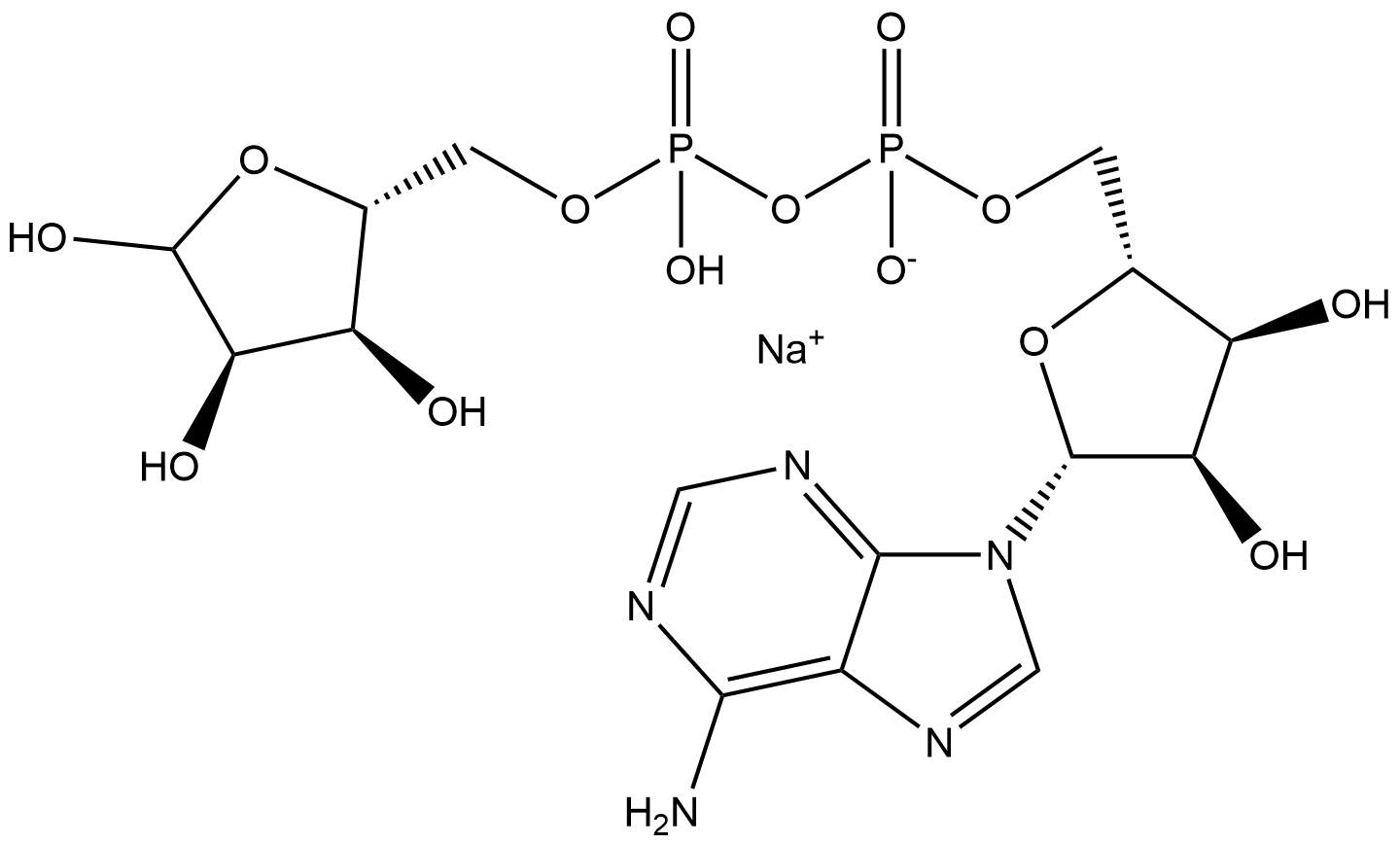 68414-18-6 結(jié)構(gòu)式
68414-18-6 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
腺苷5'-二磷酸核糖鈉
ADP ribose sodium
adenosine 5'-diphosphoribose sodium
ADENOSINE 5'-DIPHOSPHORIBOSE SODIUM SALT
Adenosine 5'-diphosphoribose sodium salt >=93%
ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHORIBOSE SODIUM SALT DIHYDRATE
ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHORIBOSE SODIUM SALT 2-HYDRATE
[[5-(6-AMINOPURIN-9-YL)-3,4-DIHYDROXYOXOLAN-2-YL]METHOXY-HYDROXYPHOSPHORYL] (2,3,4-TRIHYDROXY-5-OXOPENTYL) HYDROGEN PHOSPHATE,SODIUM
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報價日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號 | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號 | 包裝 | 價格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-100973A | 腺苷5'-二磷酸核糖鈉 Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium | 68414-18-6 | 5 mg | 750元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-100973A | 腺苷5'-二磷酸核糖鈉 Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium | 68414-18-6 | 10 mM * 1 mLin Water | 959元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-100973A | 腺苷5'-二磷酸核糖鈉 Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium | 68414-18-6 | 10mg | 1050元 |
常見問題列表
TRPM2 channel
Autophagy
In mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), H
2
O
2
treatment demonstrates that the activation of poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) produced Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose (ADP ribose), which is an activating signal for TRPM2 channels, thereby promoting Ca
2+
elevation through extracellular Ca
2+
influx and (or) lysosomal Ca
2+
release. This process eventually activates early or late autophagy in response to different degrees of oxidative stress.
TRPM2 channels are activated by binding of Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose (ADP ribose) to the intracellular NUDT9-homology (NUDT9-H) domain unique to TRPM2 and located at its C terminus. In addition to ADPR, intracellular Ca
2+
is an essential coactivator: TRPM2 channels open only in the combined presence of both ligands.
