332108-65-3
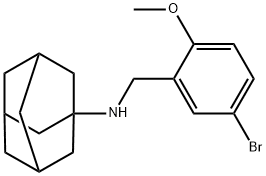 332108-65-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
332108-65-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
物理化學性質(zhì)
常見問題列表
Intracellular bacteria
Viruses
Parasite
ABMA protects cells against four bacterial toxins (
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
(DT; EC
50
of 62.9 μM),
Bacillus anthracis
(LT),
Clostridium difficile
toxin B (TcdB; EC
50
of 73.3?μM),
Clostridium sordellii
lethal toxin (TcsL; EC
50
of 86.7 μM)), three viruses (Ebola (EC
50
of 3.3?μM), rabies (EC
50
of 19.4?μM), dengue-4 virus ( EC
50
of 8.2?μM)), two species of Chlamydiales intracellular bacteria (
Simkania negevensis
and
Chlamydia trachomatis
), and the parasite
Leishmania infantum
(EC
50
of 7.1?μM) at micromolar level.
In A549 cells, ABMA treatment induces a decrease in ricin cytotoxicity with an EC
50
of 3.8?μM, and a protection factor (R) at 30?μM ranging from 5 to 10. ABMA retained almost 100% of its biological activity against ricin-induced cytotoxicity up to six days.
ABMA (2-200 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; female BALB/c mice) treatment protects mice from nasal instillation of an LD 90 of ricin.
| Animal Model: | Pathogen-free female BALB/c mice (6 week-old) with ricin |
| Dosage: | 2 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg |
| Administration: | Intraperitoneal injection |
| Result: | A statistically significant protection according to survival curves was observed with a single ip dose of 2?mg/kg. The 20?mg/kg dose fully protected animals through to day 21. The 200?mg/kg dose resulted in 80% of protection of mice against ricin challenge with a single animal succumbing on day 15. |