218600-44-3
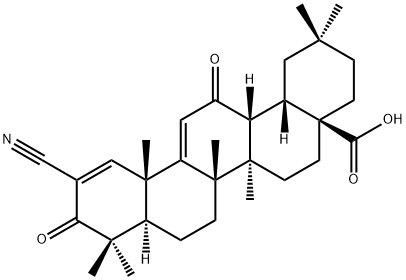 218600-44-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
218600-44-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
齊墩果烷三萜化合物
NRF-2激活劑(BARDOXOLONE)
2-氰基-3,12-二氧代齊墩果-1,9-二烯-28-酸
2-氰基-3,12-二氧代齊墩果-1,9-二烯-28-酸, 一種新型核調(diào)節(jié)因子 (NRF-2)激活劑
CDDO
CS-321
RTA 401
Bardoxolone
RTA-401
RTA401
CDDO(Bardoxolone)
Bardoxolone (CDDO)
bardoxolone RTA 401
BARDOXOLONE
CDDO
RTA 401
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2025/02/05 | S6647 | 2-氰基-3,12-二氧代齊墩果-1,9-二烯-28-酸 Bardoxolone | 218600-44-3 | 5mg | 970.53元 |
| 2025/02/05 | S6647 | 2-氰基-3,12-二氧代齊墩果-1,9-二烯-28-酸 Bardoxolone | 218600-44-3 | 25mg | 2970.62元 |
常見問題列表
| Target | Value |
|
Nrf2
() |
Bardoxolone methyl, a novel synthetic triterpenoid and antioxidant inflammation modulator, potently induces Nrf2 and inhibits NF-κB and Janus-activated kinase/STAT signaling. Bardoxolone methyl has been shown to induce differentiation, inhibit proliferation, and induce apoptosis in cancer cell lines.
Kidney sections from Bardoxolone methyl-treated monkeys demonstrates decreased megalin protein expression despite similar mRNA expression across groups. The visualized decrease in megalin protein expression is confirmed by densitometry analyses, which demonstrated that Bardoxolone methyl administration significantly decreased megalin protein expression in the monkey kidney. Bardoxolone methyl administration does not affect the protein expression of cubilin in the kidney or the mRNA expression of cubilin in the kidney. The creatinine clearance in monkeys administered Bardoxolone methyl significantly differed from that at baseline and in vehicle-treated animals on day 28. After 28 days of Bardoxolone methyl administration, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratios (UACRs), determined from the 24-hour urine collections, are significantly increased compared with those in animals receiving vehicle. Of note, UACRs decreases 53.3% in vehicle-treated animals and increased 27.9% in Bardoxolone methyl-treated monkeys. Male C57BL/6J mice are administered oral BARD during HFD feeding (HFD/BARD), only fed a high-fat diet (HFD), or fed low-fat diet (LFD) for 21 weeks. Compared with LFD mice, HFD mice have a marked increase in the number of F4/80 crown-like structures (+95%; p<0.001), which is effectively prevented by BARD (?50%; p<0.01). Similarly, the number of F4/80 interstitial macrophages is significantly higher in HFD mice by 98% (p<0.001) compared with LFD mice and by 32% (p<0.01) compared with HFD/BARD mice.
