| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone | [CAS]
9003-39-8 | [Synonyms]
POP
k25
k60
PVP
pvp2
pvp3
pvp4
pvp5
pvp6
pvp7
k115
K-30
PVPD
143rp
at717
mpk90
PVP-17
hemodez
bolinan
agrimer
pvp-k15
pvp-k60
toxobin
vinisil
subtosan
PVP K120
PVP H-30
albigena
aldacolq
PLASDONE
PLANT AC
PVP K-30
POVIDONE
luviskol
kollidon
periston
peviston
KoVidone
A-PVP,PVP
plasdone4
plasmosan
peragalst
peregalst
ncic60582
ganexp804
hemodesis
protagent
polyclarh
polyclarl
polyclarat
agentat717
ganexp-804
POLYVIDONE
nci-c60582
kollidon17
kollidon25
kollidon30
periston-n
luviskolk30
luviskolk90
POLYVIDONUM
PLASDONE XL
K30 PVP K30
PVP 3600000
PlasdonePVP
POVIDONE(RG)
cross-linked
CarboTab PVP
CROSPOIRDONE
POVIDONE USP
k25(polymer)
k25[polymer]
k30(polymer)
k30[polymer]
k60(polymer)
neocompensan
PVP K30 USP24
PVPK30Povidone
plasdonek29-32
plasdonek-26/28
k115(polyamide)
povidone(uspxix)
Polyvidoneiodine
Povidone PVP K 30
POVIDONE,K-30,FCC
POVIDONE,K-90,FCC
POVIDONE,K-90,USP
POLYCLAR ATPRACT.
Povidone (100 mg)
Povidone K-17, USP
POLYVIDONE 25 1 KG
P.V.P(povidone) Bp
POLYVIDONE 25 100 G
Crospovidone ~40,000
PoIyvinylpyrrolidone
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE
Polyvidone, Povidone
Crospovidone (100 mg)
Crospovidone (200 mg)
Polyvidone Povidone PVP
polyvinylpolypyrolidone
vinylpyrrolidonepolymer
PVP K 30 TECHNICAL GRADE
PVP-K Homopolymer Series
PolyvinylpyrrolidoneK-17
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone POP
Poly-1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidon
Pvp(PolyvinylPyrrolidone)
VP/VA copolymer PVP-VA
K 30 POVIDONE K 30 BP/USP
vinylpyrrolidinonepolymer
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 15
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 25
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 30
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 90
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 60
poly(n-vinylbutyrolactam)
n-vinylpyrrolidonepolymer
n-vinylbutyrolactampolymer
poly(1-vinylpyrrolidinone)
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)
n-vinylpyrrolidinonepolymer
polyvinypyrrolidone PVP-K
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, avera
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP10)
vinylpyrrolidone homopolymer
PVPP,Povidon:MW29.000,powder
PVPP,Povidon:MW10.000,liquid
PVPP,Povidon:MW55.000,powder
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONEPOLYMERS
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)
1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone polymer
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE 90PRACT.
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE 15PRACT.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone solution
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 15
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30, FCC
1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinonpolymers
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE (PVP-K30)
polyvinylpyrrolidone, povidone
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 25, USP
povidone(polyvinylpyrrolidone)
PVPP,Povidon:MW1.300.000,powder
Polyvinylpyrrolidone,M.W.40,000
polyvinylpyrrolidone, m.w. 8,000
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE-DIVERGAN RS
1-ethenyl-2-pyrrolidinonepolymers
POLYVINYLPOLYPYRROLIDONE (PVP-40)
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 30, POWDER
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 90, POWDER
polyvinylpyrrolidone, m.w. 630,000
1-ethenyl-2-pyrrolidinonhomopolymer
polyvinylpyrrolidone, m.w. 1,300,000
POLYVINYLPOLYPYRROLIDONE DIVERGAN RS
Polyvinylpyrolidone PVP/PA Copolymer
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE (K30) (POVIDONE)
2-pyrrolidinone,1-ethenyl,homopolymer
2-Pyrrolidinone,1-ethenyl-,homopolymer
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE, AVE. M.W. 10,000
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (MW 1.3 Million)
Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 10,000
POLY(N-VINYL-2-PYRROLIDONE) (LOW M.WT.)
POLY(N-VINYL-2-PYRROLIDONE) (MED. M.WT.)
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)homopolymer
undissolve polyvinylpolypyrolidone(PVPP)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 58,000
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone POP 5g [9003-39-8]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone average Mol wt 10,000
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE, AVERAGE MW CA.29,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone/povidone(pharm grade)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone average mol wt 360,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 30, average Mw 40,000
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE, AVERAGE MW CA. 55, 000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 3500, K12
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, molecular biology grade
Polyvinylpyrrolidone,PVP, Polyvidone, Povidone
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE PLANT CELL CULTURE TESTED
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE MOLECULAR BIOLOGY*R EAGENT
Polyvinylpyrrolidone powder, average Mw ~29,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone powder, average Mw ~55,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone average Mw ~1,300,000 by LS
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 60 SOLUTION, 45% IN WATER
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 8.000, K16-18
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.1
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.2
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.3
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.4
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.5
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.6
poly(1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone)hueper’spolymerno.7
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 58.000, K29-32
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE (K90) MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GRADE
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, Avg. M.W. Approx. 40,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 8,000, K 15-19
Polyvinylpyrrolidone,M.W.400,000,45%AqueousSolution
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 1.300.000, K85-95
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE AV. MOL.*WT. 40,000 EMBRYO TES
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE, AVERAGE MW CA. 1,3 00,000 (LS)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 90, powder, average Mw 360,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 15 Average Molecular Wt. 10,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 30 Average Molecular Wt. 40,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 25, tested according to Ph.Eur.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 90 Average Molecular Wt. 360,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 58.000, K29-32 100GR
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 58.000, K29-32 500GR
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 1.300.000, K85-95 1KG
POLYVINYLPYRROLIDONE K 90, FOR MOLECULAR BIOLOGY, POWDER
Polyvinylpyrrolidone, average M.W. 1.300.000, K85-95 500GR
Polyvinylpyrrolidone solution K 60, 45% in H2O, Mr ~160000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone,‘Plasdone’, PVP, Polyvidone, Povidone
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 15 Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 10,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 30 Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 40,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 90 Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 630,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone Vetec(TM) reagent grade, average mol wt 10,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone Vetec(TM) reagent grade, average mol wt 40,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone Vetec(TM) reagent grade, average mol wt 360,000
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 60 Average Molecular Wt. 160,000
(ca. 35% in Water)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 60 Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 220,000 (45% in Water)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 60 Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 220,000 (ca. 35% in Water)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone K 60 Viscosity Average Molecular Wt. 220,000 (ca. 35% in Water), 000 (ca. 35% in Water) | [EINECS(EC#)]
1312995-182-4 | [Molecular Formula]
(C6H9NO)n | [MDL Number]
MFCD00149016 | [MOL File]
9003-39-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
16.0425 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white powder | [Melting point ]
~165 °C (dec.)(lit.)
| [Boiling point ]
90-93 °C | [bulk density]
330kg/m3 | [density ]
1,69 g/cm3 | [Tg]
175 | [refractive index ]
(25) 1.5300 | [refractive index ]
1.5300 | [storage temp. ]
Store at RT. | [solubility ]
H2O: soluble100mg/mL | [form ]
powder
| [color ]
White to yellow-white | [PH]
3.0-5.0 | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Light sensitive. Hygroscopic. | [biological source]
synthetic (oragnic) | [Water Solubility ]
Soluble in water. | [Sensitive ]
Hygroscopic | [Merck ]
14,7697 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C8H15NO/c1-3-7(2)9-6-4-5-8(9)10/h7H,3-6H2,1-2H3 | [Contact allergens]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone is widely used as is in cosmetics
such as hair care products and in medical products. It
acts as iodophor in iodine-polyvinylpyrrolidone. PVP
is an irritant and has been claimed as the allergen in
some cases of dermatitis from iodine-polyvinylpyrrolidone
(although iodine is more likely the hapten). It
may cause type I contact urticaria or anaphylaxis. | [InChIKey]
FAAHNQAYWKTLFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
N1(C(C)CC)C(=O)CCC1 | [IARC]
3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7, 71) 1987 | [EPA Substance Registry System]
2-Pyrrolidinone, 1-ethenyl-, homopolymer(9003-39-8) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white powder | [Usage]
suitable for gene delivery | [Definition]
ChEBI: A vinyl polymer composed of repeating -CH2-CRunits where R is a 2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl group. | [General Description]
White powder. Compatible with a wide range of hydrophilic and hydrophobic resins. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Hygroscopic. Water soluble. | [Reactivity Profile]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone is a polymeric material and probably has low reactivity. Polyvinylpyrrolidone reacts as a weak base. | [Health Hazard]
SYMPTOMS: Polyvinylpyrrolidone may cause interstitial fibrosis in the lungs. Lesions regress when patient is no longer being exposed to the compound. | [Fire Hazard]
Flash point data for Polyvinylpyrrolidone are not available, but Polyvinylpyrrolidone is probably non-flammable. | [Hazard]
Questionable carcinogen.
| [Preparation]
N-Vinylpyrrolidone is prepared from 1,4-butanediol as follows:
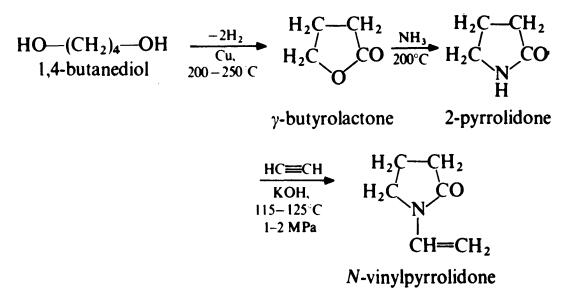
N -Vinylpyrrolidone is water-soluble and is usually polymerized in aqueous solution at about 50??C with ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. The polymer
is also water-soluble and is isolated by spray-drying. Commercial grades of
polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) have average molecular weights (Mv) ranging
from about 10000 up to 360000.
The largest use of polyvinylpyrrolidone is in cosmetic formulations, especially hair lacquers. In the latter applications, polyvinylpyrrolidone is the
preferred film-former on account of good adhesion to hair, lustre of the film
and ease of removal on washing. The polymer is also used as a binder in
pharmaceutical tablets. Polyvinylpyrrolidone also finds use in the textile
industry, particularly in colour stripping operations, where the great affinity
of the polymer for dyestuffs is utilized. An interesting application of poly�vinylpyrrolidone is in aqueous solution as a blood plasma substitute; such
material was extensively used in Germany during the Second World War. | [Production Methods]
Povidone is manufactured by the Reppe process. Acetylene and
formaldehyde are reacted in the presence of a highly active copper
acetylide catalyst to form butynediol, which is hydrogenated to
butanediol and then cyclodehydrogenated to form butyrolactone.
Pyrrolidone is produced by reacting butyrolactone with ammonia.
This is followed by a vinylation reaction in which pyrrolidone and
acetylene are reacted under pressure. The monomer, vinylpyrrolidone,
is then polymerized in the presence of a combination of
catalysts to produce povidone. | [Brand name]
Kollidon CL (BASF); Kollidon CLM (BASF); Polyplasdone (International Specialty Products);Acu-dyne;Adapettes;Adsorbobase;Adsovbotear;Agent at 717;Albigen a;Aldacol q;Amiorel eritro;Amyderm s;Andrestrac 2-10;Anexa;B 7509;Betaisod;Bridine;Clinidine;Final step;Frepp/sepp;Ganex p 804;Ga-pvp-101;Gyno-bidex;Isoplasma;Jodoplex;K 115;Kollidon 17;Kollidon 25;Kollidon 30;Kollidon 90;Kollidon ce 50/50;Kollidon k 25;Kollidon k 30;Luviskol k 17;Luviskol k 25;Luviskol k 30;Luviskol k 90;Luvisteol;Medicort;Molycu;Mundidon;Neojodin;Oftan flurekain;Peragal st;Periston-n-toxobin;Pevidine;Plasmadone;Plasmoid;Plassint;Podiodine;Polyclar at;Polyclar h;Polyclar l;Polyplasdone xl;Polyvidone-escupient;Polyvinyl pyrrolidone;Povadyne;Povidone k 29-32;Pvp 50;Pvp0;Pvp-k 15;Pvp-k 25;Pvp-k 30;Pvp-k 60;Pvp-k 90;Pvp-macrose;Pvp-macrox;Rocmuth;Sd 13;Soft-care;Tears plus;Venostasin retard;Vetedine;Yodiplexin. | [World Health Organization (WHO)]
Polyvidone, a polymer of vinylpyrrolidinone, is an excipient used
as a suspending and dispersing agent. Injectable preparations containing polymers
with a molecular weight in the order of 12,000 have caused painful local granulomatous lesions. This has led to the withdrawal of polyvidone from such
preparations in some countries. Polyvidone was formerly also used as a plasma
expander but, because it was sequestered within the liver and spleen, this use has
been discontinued. However, it remains widely used as a vehicle for ophthalmic
preparations, and as the major component of artificial tears. | [Pharmaceutical Applications]
Although povidone is used in a variety of pharmaceutical
formulations, it is primarily used in solid-dosage forms. In tableting,
povidone solutions are used as binders in wet-granulation
processes.Povidone is also added to powder blends in the dry
form and granulated in situ by the addition of water, alcohol, or
hydroalcoholic solutions. Povidone is used as a solubilizer in oral
and parenteral formulations, and has been shown to enhance
dissolution of poorly soluble drugs from solid-dosage forms.
Povidone solutions may also be used as coating agents or as binders
when coating active pharmaceutical ingredients on a support such
as sugar beads.
Povidone is additionally used as a suspending, stabilizing, or
viscosity-increasing agent in a number of topical and oral
suspensions and solutions. The solubility of a number of poorly soluble active drugs may be increased by mixing with povidone.
Special grades of pyrogen-free povidone are available and have
been used in parenteral formulations; | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone can bind to polyphenol. Thus, it is known to be used for RNA isolation from plants rich in polyphenols. It is extensively used in the synthesis of nanoparticles. | [Solubility in organics]
alcohols, amines, chloroform, glycols, methylene chloride, nitroparaffins, water (cold) | [storage]
Povidone darkens to some extent on heating at 150°C, with a
reduction in aqueous solubility. It is stable to a short cycle of heat
exposure around 110–130°C; steam sterilization of an aqueous
solution does not alter its properties. Aqueous solutions are susceptible to mold growth and consequently require the addition of
suitable preservatives.
Povidone may be stored under ordinary conditions without
undergoing decomposition or degradation. However, since the
powder is hygroscopic, it should be stored in an airtight container in
a cool, dry place. | [Purification Methods]
Purify it by dialysis, and freeze-drying. Also by precipitation from CHCl3 solution by pouring into ether. Dry it in a vacuum over P2O5. For the crosslinked polymer purification is by boiling for 10minutes in 10% HCl and then washing with glass-distilled water until free from Cl ions. Finally, Cl ions are removed more readily by neutralising with KOH and continued washing. | [Incompatibilities]
Povidone is compatible in solution with a wide range of inorganic
salts, natural and synthetic resins, and other chemicals. It forms
molecular adducts in solution with sulfathiazole, sodium salicylate,
salicylic acid, phenobarbital, tannin, and other compounds; see
Section 18. The efficacy of some preservatives, e.g. thimerosal, may
be adversely affected by the formation of complexes with povidone. | [Toxics Screening Level]
The initial threshold screening level (ITSL) for polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) is being established
at 4 μg/m3 based on an annual averaging time. | [Regulatory Status]
Accepted for use in Europe as a food additive. Included in the FDA
Inactive Ingredients Database (IM and IV injections; ophthalmic
preparations; oral capsules, drops, granules, suspensions, and
tablets; sublingual tablets; topical and vaginal preparations).
Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included
in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Safety Statements ]
22-24/25 | [WGK Germany ]
1
| [RTECS ]
TR8370000
| [Autoignition Temperature]
440 °C | [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
39059990 | [Safety Profile]
Mtldly toxic by
intraperitoneal and intravenous routes.
Questionable carcinogen. When heated to
decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. | [Hazardous Substances Data]
9003-39-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Vinylpyrrolidone polymer]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone is abbreviated as PVP, and is the polymer of vinylpyrrolidone. According to the different degree of polymerization, it is further classified into soluble PVP and insoluble PVPP (polyvinyl polypyrrolidone). Molecular weight of the soluble PVP is 8,000 to 10,000.The soluble PVP can be used as a precipitating agent which can be settle down through its action with polyphenols. Using this method, it is easily to have residual PVP in the alcohol. Due to the savings effect of PVP inside the human body, the World Health Organization doesn’t recommend to apply this substance. In recent years, the use of soluble PVP has been rare. Insoluble PVPP system had began to be used in the beer industry since the early 1960s. It has a relative molecule weight greater than the relative mass greater than 700,000. It is a insoluble polymer derived from the further cross-linking and polymerization of PVP and can be used as an adsorbent of polyphenols with a good efficacy.
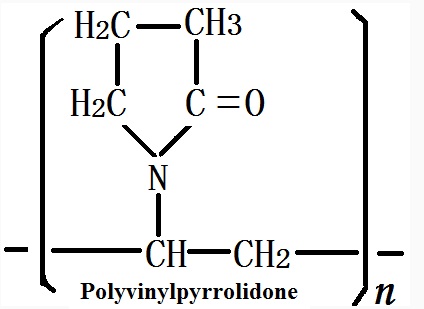
The molecular formula of Polyvinylpyrrolidone
Polyvinylpyrrolidone PVP is one of the three major pharmaceutical new excipients and can be used as the co-solvent of tablets, granules, and injection, as the glidant of capsules, as the dispersant agent of liquid preparations and the colorant, as the stabilizer of enzyme and heat sensitive drug, as the co-precipitating agent of poorly soluble drugs, and as the detoxicant of ophthalmic drugs and lubricants.
It is industrially used as expanded polystyrene additive, as the gelling agents for suspension polymerization, stabilizer, and fiber treating agents, paper processing aids, adhesives, and thickening agents.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone PVP and its copolymers CAP is an important raw material of cosmetics, mainly used for hair retaining agent. The film it formed in the hair is elastic and shiny, and has excellent carding property as well as being free of dust. Adopting different category of resin can meet various kinds of relative humidity climatic conditions. Therefore, it is an indispensable raw material in styling hair cream, hair gel, and mousse. It can also be used for the cosmetics of skin moisturizing agents and the dispersants for grease based hair dying, also as foam stabilizers, and can improve the consistency of the shampoo.
Insoluble PVP is the stabilizer of beer and juice which can improve its transparency, color, and flavor.
| [Water-soluble polyamides]
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) is a water soluble polyamide. Commercially available PVP is divided into four viscosity grades according to its press K value (Fikentscher K value): K-15, K-30, K-60, K-90, with the average molecular weight being 10,000, 40000,160000, and 360000, respectively. K value or molecular weight is an important factor which decides the various properties of PVP.
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) is dissolved in water, chlorinated solvents, alcohol, amine, nitro-paraffin and low molecular weight fatty acids, and is mutually soluble with most inorganic salts and a variety of resin; insoluble in acetone and ether. PVP used for the matrix of dropping pill matrix is odorless, tasteless, white to pale yellow waxy solid with the relative density being 1.062, and its 5% aqueous solution pH being 3 to 7. PVP is hygroscopic and of good thermal stability, and can be dissolved in various kinds of organic solvents, and has high melting point. Adding certain natural or synthetic polymers or organic compounds can effectively adjust the PVP’s hygroscopicity and softness. PVP is not prone to have chemical reaction. Under normal storage conditions, dry PVP is quite stable. PVP has excellent physical inertia and biocompatibility and has not stimulation to skin, eyes no stimulation with no allergic reactions and being non-toxic.
Because of the hydrogen bonding or complexation effect, PVP’s viscosity is increased and this further inhibits the formation and growth of crystallized nuclei of drugs, making the drug being in the amorphous state. The dropping pill whose matrix is PVP can enhance the dissolution and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. In general, the greater the PVP amount, the higher dissolution and solubility of drug in the medium. Susana et al have studied the dissolution of the PVP solid dispersant of the slightly soluble drug albendazole. The increased amount of PVP (k30) can increase the dissolution rate and efficiency of drug inside the solid dispersant. Teresa et al have studied the dissolution of the poorly soluble drugs, flunarizine in PVP solid dispersant and obtained similar conclusion. PVP also found that the higher the content, the more significant increase in dissolution. IR has showed that flunarizine and PVP has no chemical reaction except in some cases that a best dissolution efficacy is obtained only in certain ratio between some drugs with the PVP. Tantishaiyakul et al has found that: when the ratio of piroxicam: PVP is 1:5 and 1:6, the dissolution of the solid dispersant is the largest with a 40 times as high as that of single drug within 5min.
PVP can also be dissolved in another molten dropping pill matrix, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyoxyethylene monostearate (S-40), poloxamer and stearyl acid, glyceryl monostearate, etc for making complex matrix.
The above information is edited by the Chemicalbook of Dai Xiongfeng.
| [Physical and chemical properties]
Commonly used PVP level in the cosmetic industry is K-30. Commercialized PVP is white and free flowing powder or solids with its content in the mass fraction of 20%, 30%, 45% and 50% aqueous solution. PVP is soluble in water and is hygroscopic with a moisture equilibrium being 1/3 of the relative humidity of the environment. Similar as the protein hydration action, each monomer associates with 0.5mol water.Chart 1 and Chart 2 lists the reference quality standard of various types of polyvinylpyrrolidone PVP:
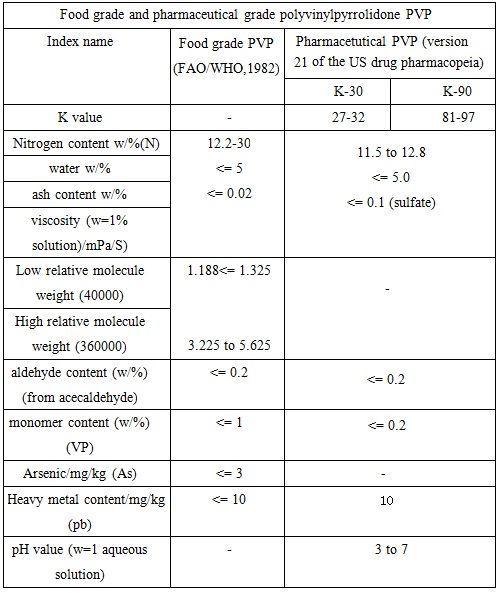
Chart 1: Food grade and pharmaceutical grade polyvinylpyrrolidone PVP
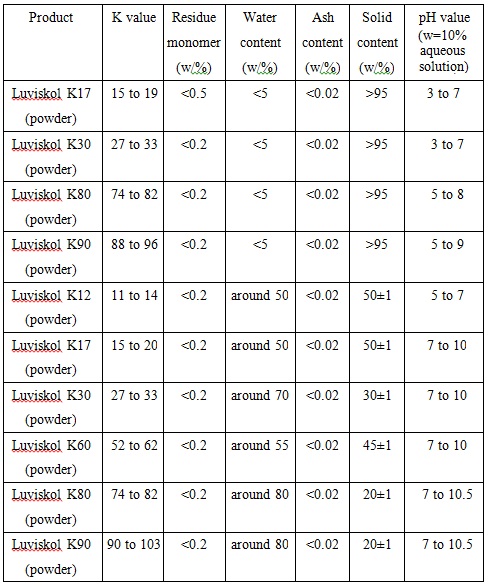
Chart 2: Cosmetics and industrial polyvinylpyrrolidone PVP (Luvikol K, BASF)
PVP is not easy to have chemical reaction. When stored at normal conditions, dry PVP is quite stable. Solution undergone mildew treatment is also stable. When heated in air to 150 °C or mixed with ammonium persulfate to heat at 90 °C for 30min, PVP will be exchanged to become a water-insoluble compound. In the presence of azo compound or a dichromate oxidizing agent, light will cause PVP solution to become gel. The co-heating of PVP solution with strong base (such as sodium silicate or trisodium phosphate) will generate precipitation. Many different compounds can generate complexes with PVP. For example, the complexes of PVP and iodine is very stable and have a good bactericidal effect and can reduce its toxicity; Adding the copolymers of the polyacrylic acid, tannic acid or methyl vinyl ether and maleic acid to the aqueous solution of PVP will generate insoluble complexes which are insoluble in water, alcohols and ketones. But when being treated with base for neutralize the poly-acid can reverse the reaction; complexation between PVP and toxins, drugs and toxic chemicals can reduce their toxicity; some kinds of dyes can also form a strong complex with PVP, which is the basis for using PVP as a dye bleaching agent.
| [The use of polyvinylpyrrolidone]
In the early 1950s, older, with shellac and oil-based hairspray had been rapidly replaced by PVP sprays which are still widely used until now. It can form wet, transparent film on the hair which is shiny and has good lubrication effect. PVP has good compatibility with a variety of good propellant and also has corrosion resistance. It is widely used in hair styling, as the film former in combing products, as the creatinine and stabilizer of skin care lotions and creams, as the base stock material for eye and facial cosmetics and lipstick base, and also as hair dye dispersants and shampoo foam stabilizer. PVP has detoxification effect and can reduce the irritation effects of other preparation on the skin and eyes. It is also used as toothpaste detergents, gelling agents and antidotes. The main drawback of PVP is its sensitivity to moisture. However, this issue can be tackled by using its vinyl acetate copolymer in order to mitigate the effects of moisture and humidity. In addition, PVP also has wide application in the pharmaceutical, beverage and textile industries.
| [Rheological properties of solutions]
Water and methanol is the preferred solvent of PVP. pH value has little effect on the viscosity of the aqueous solution of PVP, for example, at 25 °C, pH range: 0.1~10, aqueous solution of PVP K-30 with a mass fraction of 5% concentration has a viscosity of 2.3~2.4mPa ? s; in concentrated hydrochloric acid, this is 4.96mPa ? s. Effect of temperature on the viscosity of the PVP aqueous solution is also relatively not obvious. Un-cross-linked PVP solution is not particularly thixotropic unless under very high concentration and display a short relaxation time. The chart 3 below lists the viscosity of PVP K-30 in a variety of solvents.
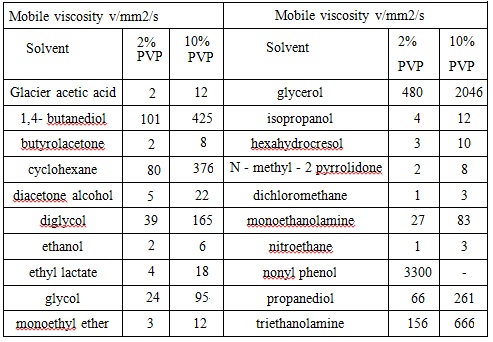
Chart 3: Viscosity of PVP K-30 in various organic solvents (w %) (At room temperature)
Reference: Edited by Binyi Qiu, “Compendium of cosmetic chemistry and technology” Volume 1 Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 1997.
| [Compatibility]
Polyvinylpyrrolidone is mainly used as pharmaceutical excipient, blood compatibilizer, cosmetics thickening agents, latex stabilizers, and clarifying agent of beer brewing.
Not matter whether in solution or in the form of film, PVP always has a high degree of compatibility. It has good compatibility with various kinds of inorganic salt solution, many natural and synthetic resins and other chemical compatibility. Examples of their compatibility are seen at chart 4 and Figure 5.
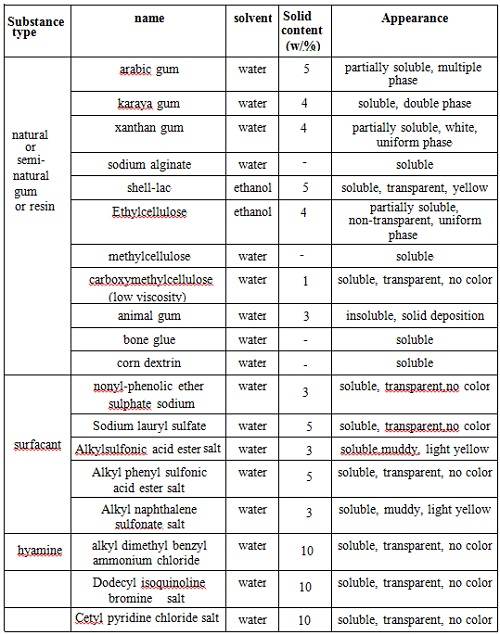
Chart 4: The compatibility of PVP and some other substances in water and ethanol
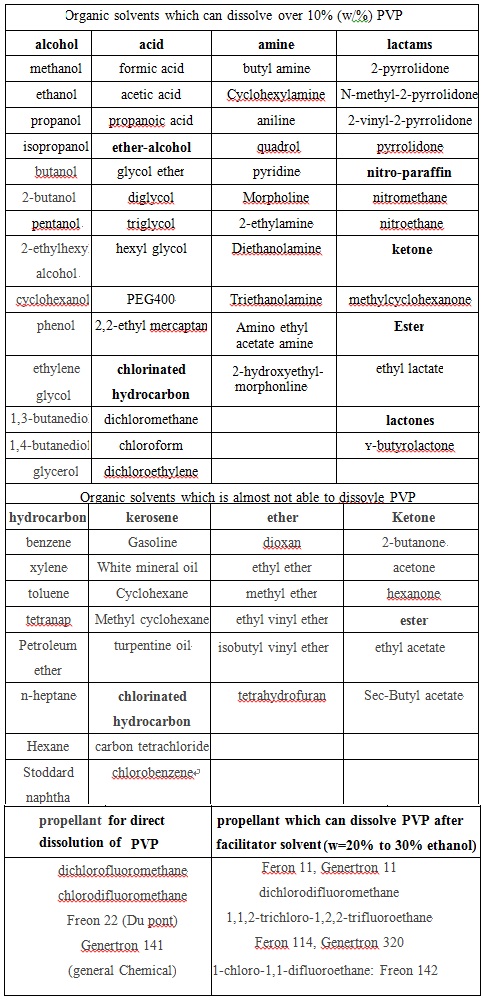
Chart 5: The solubility and compatibility of PVP in various solvents
| [Safety]
PVP is physiologically inert. Acute oral toxicity of PVP: LD50 > 100g/kg. It does not irritate the skin or eyes, do not cause skin allergies. A large number of long-term toxicology studies have confirmed that polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) can tolerate intraperitoneal, intramuscular, intravenous administration and parenteral applications. Subacute and chronic toxicity result was negative.
| [Identification test]
Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol and chloroform and insoluble in ether. This is measured by the OT-42 method.
Dichromate precipitation test: in 5 mL of2% sample solution, add 5 mL dilute hydrochloric acid solution (TS-117), further add 5 mL of water plus 2 mL of 10% potassium dichromate solution and 2ml. This should form an orange precipitate.
Take 75 mg of cobalt nitrate and 300 mg of ammonium thiocyanate for being dissolved in 2ml of water; add 5 mL of 2% aqueous sample solution; after the mixing, add dilute hydrochloric acid test solution (TS-117) for acidification. This should form light blue precipitate.
Take 5 mL of 2% sample solution; add 1 mL of 25% hydrochloric acid, 5 mL of 5% barium chloride and 1 mL 5% molybdenum tungsten phosphoric acid solution. This should generate a lot of white precipitate which gradually turns blue in the sunlight.
The pH value of 5% sample solution should be 3.0 to 3.7. This is measured by conventional means.
Adding a few drops of iodine test solution (TS-124) to 5 mL of 0.5% sample solution should produce a deep red color.
Take 1 g of sample, add water to 10 ml as a suspension, add 0.1 mL of iodine test solution (TS-124), after mixing by shaking for 30s, iodine test solution should fade (to distinguish polyvinylpyrrolidone due to that polyvinylpyrrolidone can form red color). Add 1 mL of starch test solution (TS-235), after shaking and mixing, there should be no blue color formed. to produce blue.
| [Content Analysis]
Estimated from the nitrogen content according to the following index of quality.
| [Toxicity]
ADI 0~50 (FAO/WHO, 2001)
LD50> 100g/kg (rat, oral).
ADI does not make special provision (FAO/WHO, 2001).
It is safe for food (FDA, §121.1110, §173.50, 2000).
LD50:12g/kg (mice, abdominal injection).
| [Limited use]
GB 2760-1996: beer GMP.
| [Chemical Properties]
It is the cross-linked homopolymer of pure vinylpyrrolidone. It is hygroscopic and free-flowing white or off-white powder. It has a slight foul smell. It is insoluble in common solvents such as water, ethanol and ether. So its molecule weight range can’t be measured. However, PVP has ability to form complex with various kinds of substances (such as “Hu” class substance which can lead to the discoloration of a variety of wines and beverages discoloration). Also it is easily to be removed after filtration because of its insolubility.
| [Uses]
Clarifying agent; pigment stabilizer; colloidal stabilizer; It is mainly used for beer clarifying and quality stabilizing (reference amount 8~20g/100L, maintained for 24h and remove it by filtration), and can also be applied in combination with enzymes (protease) and protein adsorbents. It is also used to clarify the wine and as a stabilizer to prevent discoloration (reference amount 24~72g/100L).
Clarifying agents; stabilizers; thickeners agent; tablet fillers; dispersants; PVP of molecular weight 360,000 are often used as the clarifying agent of beer, vinegar, and grape wine.
Used as the fixing liquid for gas chromatography.
It is used as a colloidal stabilizer and clarifying agent for beer clarification. Apply proper amount according the demands of production.
It can be used for pharmacy, aquaculture, and livestock disinfectant for the sterilization of the skin and mucous.
PolyFilterTM molecule has an amide bond for absorbing the hydroxyl groups located in polyphenol molecule to form hydrogen bonds, and therefore, can be used as the stabilizer of beer, fruit wine/grape wine, and drinking wine to extend their shelf life and improve the transparency, color and taste. The products have two specifications: disposable type and regeneration type. Disposable products are suitable for application by SMEs; renewable products demand the purchase of special filtration equipment; but since it is recyclable, it is suitable for large breweries for recycle application.
In daily cosmetics, PVP and its copolymer has good dispersion property and filming property, and thus being able to be used as a setting lotion, hair spray and styling mousse, as opacifiers for hair care agents, as the stabilizer of shampoo foam, as wave styling agent and as the dispersants and affinity agents in hair dye. Adding PVP to cream, sunscreen, and hair removal agent can enhance wetting and lubricating effect. Taking advantage of the excellent properties of PVP such as surface activity, film-forming and non-irritating to the skin, no allergic reactions, etc., has broad prospects in its application in hair care and skin care products.
| [Production method]
Its crude product comes from the polymerization of vinylpyrrolidone under basic catalyst or the existence of N, N'-divinyl amidine and further cross-inking reaction. Then use water, 5% acetic acid and 50% ethanol for reflux to until extract ≤50mg/kg (for over 3h).
The 30% to 60% aqueous solution of the purified 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone, in the presence of ammonia or amines and also with hydrogen peroxide as the catalyst, has cross-linking and homo-polymerization reaction at a temperature of 50 °C and subject to further purification to obtain the final product.
|
|
|