| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
neplanocin A | [CAS]
72877-50-0 | [Synonyms]
A-11079B16
neplanocin A
Neoplanocin A
3-Neplanocin A
(?)-Neplanocin A
Antibiotic A-11079B16
()-Neplanocin A Exclusive
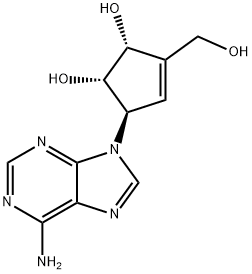
3-Cyclopentene-1,2-diol, 5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-, (1S,2R,5R)- | [Molecular Formula]
C11H13N5O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD01735607 | [MOL File]
72877-50-0.mol | [Molecular Weight]
263.25 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
214-216 °C (decomp) | [Boiling point ]
632.6±65.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.91±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
DMF: 0.2 mg/ml; DMSO: 3 mg/ml; PBS (pH 7.2): 0.3 mg/ml | [form ]
A crystalline solid | [pka]
13.43±0.70(Predicted) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
S-Adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) hydrolase catalyzes the reversible hydrolysis of SAH to adenosine and homocysteine. The inhibition of SAH hydrolase causes the intracellular accumulation of SAH, elevating the ratio of SAH to S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and inhibiting SAM-dependent methyltransferase. (−)-Neplanocin A potently and irreversibly inactivates SAH hydrolase (Ki = 8.39 nM).1 It has antitumor activity against mouse leukemia L1210 cells and broad-spectrum antiviral activity.2,3,4,1 Neplanocin A is more potent against vesicular stomatitis than the reversible SAH hydrolase inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin (ID50 = 0.07 and 0.3 μg/ml, respectively).3,5 |
|
|