| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Vorapaxar Sulfate | [CAS]
705260-08-8 | [Synonyms]
Zontivity
Sch 530348
Vorapaxar-d5
Vorapaxar Sulfate
SCH 530348 sulfate
vorapaxar impurity A
SCH-530348;SCH530348
vorapaxar monosulfate
Vorapaxar Sulfate API
SCH 530348 (H2SO4 Salt)
Vorapaxar Sulfate (SCH 530348)
N-[(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-[(1E)-2-[5-(3-Fluorophenyl)-2-pyridinyl]ethenyl]dodecahydro-1-Methyl-3-oxonaphtho[2,3-c]furan-6-yl]carbaMic Acid Ethyl Ester Sulfate
Carbamic acid, N-[(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-[(1E)-2-[5-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-pyridinyl]ethenyl]dodecahydro-1-methyl-3-oxonaphtho[2,3-c]furan-6-yl]-, ethyl ester, sulfate (1:1)
Vorapaxar sulfateQ: What is
Vorapaxar sulfate Q: What is the CAS Number of
Vorapaxar sulfate Q: What is the storage condition of
Vorapaxar sulfate Q: What are the applications of
Vorapaxar sulfate | [Molecular Formula]
C29H35FN2O8S | [MDL Number]
MFCD16038877 | [MOL File]
705260-08-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
590.66 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [storage temp. ]
4°C, away from moisture | [solubility ]
DMSO : 125 mg/mL (211.63 mM; Need ultrasonic)| (insoluble) | [form ]
Solid | [color ]
White to off-white | [Water Solubility ]
Water : < 0.1 mg/mL (ultrasonic;warming;heat to 60°C) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Merck Sharp & Dohme successfully obtained approval in the EU
in 2014 for vorapaxar sulfate, marketed as Zontivity®. The drug is a
first-in-class thrombin receptor (also referred to as a protease-activated
or PAR-1) antagonist which, when used in conjunction with
antiplatelet therapy, has been shown to reduce the chance of
myocardial infarction and stroke, particularly in patients with a
history of cardiac events. Antagonism of PAR-1 allows for
thrombin-mediated fibrin deposition while blocking thrombinmediated
platelet activation. | [Uses]
SCH-530348 is a novel antiplatelet agent undergoing development by Schering-Plough Corp for the treatment and prevention of atherothrombosis.
acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina/non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction) and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. | [Definition]
ChEBI: An organic sulfate salt obtained by combining vorapaxar with one molar equivalent of sulfuric acid. A protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist used for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction (M
) or with peripheral arterial disease. It has been shown to reduce the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke and urgent coronary revascularisation. | [Synthesis]
Although a variety of papers and patents describe the synthesis
of vorapaxar sulfate (XXXVII), a combination of two patents
describe the largest-scale synthesis reported in the literature. Retrosynthetically, the drug can be
divided into olefination partners 306 and 305. Lactone 305
is further derived from synthons 300 and 299, which are readily
prepared from commercially available starting materials. Dienyl
acid 300 was constructed in two steps starting from commercial
vinyl bromide 307, which first undergoes a Heck reaction with
methacrylate (308) followed by saponification of the ester to afford
the desired acid 300 in 71% over two steps.
The synthesis of alcohol 299 begins with tetrahydropyranyl
(THP) protection of enantioenriched alcohol 295 to afford butyne
297 . Lithiation of this system followed by trapping
with (benzyloxy)chloroformate and Dowex work-up to remove
the protective functionality provided acetyl ester 298. Hydrogenation
of the alkyne with Lindlar?ˉs catalyst delivered cis-allylic alcohol
299 in 93% yield. Acid 300 was then esterified with alcohol
299 by way of a 1,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) coupling
and, upon heating in refluxing xylenes, an intramolecular Diels¨C
Alder reaction occurred. Subsequent subjection to DBU secured
the tricyclic system 301 in 38% over three steps as a single enantiomer.
Diastereoselective hydrogenation reduced the olefin with
concomitant benzyl removal to give key fragment 302. Next, acidic
revelation of the ketone followed by reductive amination with
ammonium formate delivered primary amines 303a/303b as a
mixture of diastereomers. These amines were then converted to
the corresponding carbamates, and resolution by means of recrystallization
yielded 50% of 304 as the desired diastereomer. Acid 304
was treated with oxalyl chloride and the resulting acid chloride
was reduced to aldehyde 305 in 66% overall yield. Finally, deprotonation
of phosphonate ester 306 followed by careful addition of 305 and acidic quench
delivered vorapaxar sulfate (XXXVII) in excellent yield over the
two-step protocol.
The preparation of vorapaxar phosponate ester 306
commenced from commercial sources of 5-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-
methylpyridine (310). Removal of the methyl proton with LDA
followed by quench with diethyl chlorophosphonate resulted in
phosponate ester 306.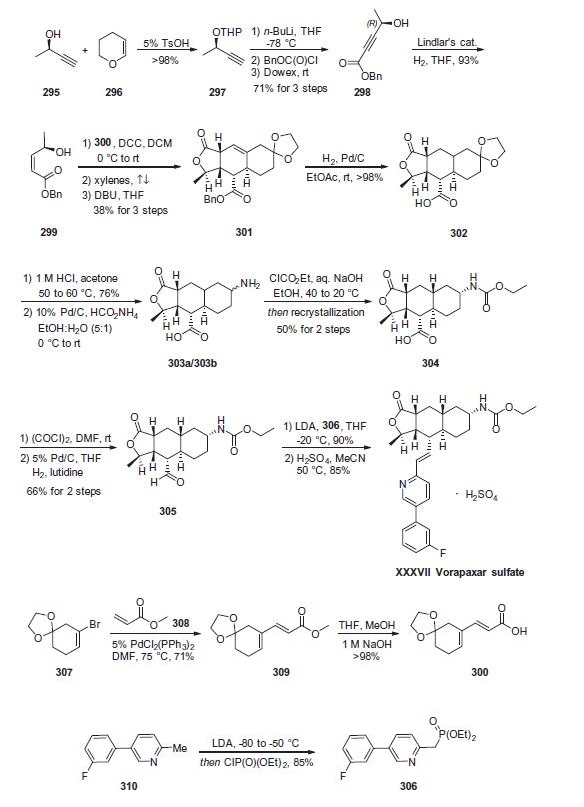
|
|
|