| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE | [CAS]
69-05-6 | [Synonyms]
erion
sn390
mecryl
866r.p.
palusan
pentilen
palacrin
erionHCl
italchin
metochin
metoquin
ATABRINE
MEPACRINE
metoquine
chinacrin
crinodora
NSC 14229
malaricida
chemiochin
methoquine
QUINACRINE
quinacrine2HCl
Quinacrine, DiHCl
ERION HYDROCHLORIDE
ARICHIN HYDROCHLORIDE
ATEBRIN HYDROCHLORIDE
METOCHIN HYDROCHLORIDE
ATABRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Atebrine hydrochloride
quinacrinehydrochloride
ATEBRIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE
CHINACRIN HYDROCHLORIDE
atabrinedihydrochloride
CHEMIOCHIN HYDROCHLORIDE
MEPACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE
Quinacine dihydrochloride
QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE
DL-QUINACRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
MEPACRINE HYDROCHLORIDE USP
Quinacrine Dihydrochloride
DL-QUINACRINE HYDROCHLORIDE USP
Quinacrine Dihydrochloride Hydrate
QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE CRYSTALLINE
QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE MAO INHIBITOR
QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE, FOR FLUORESC ENCE
2-chloro-5-(omega-diethylamino-alpha-methylbutylamino)-7-methoxyacridinedihy
2-methoxy-6-chloro-9-(4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamino)acridinedihydrochlor
3-chloro-7-methoxy-9-(1-methyl-4-diethylaminobutylamino)acridinedihydrochlor
3-chloro-9-(4’-diethylamino-1’-methylbutylamino)-7-methoxyacridinedihydrochl
6-CHLORO-9-(4-DIETHYLAMINO-1-METHYL-BUTYLAMINO)-2-METHOXYACRIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE
3-Chloro-7-methoxy-9-[1-methyl-4-(diethylamino)butylamino]acridine dihydrochloride
6-CHLORO-9-(4-DIETHYLAMINO-1-METHYL-N-BUTYL)AMINO-2-METHOXYACRIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE
2-Methoxy-6-chloro-9-[[4-(diethylamino)-1-methylbutyl]amino]acridine dihydrochloride
3-Chloro-9-[4'-(diethylamino)-1'-methylbutyl]amino]-7-methoxyacridine dihydrochloride
1,4-Pentanediamine, N4-(6-chloro-2-methoxy-9-acridinyl)-N1,N1-diethyl-, dihydrochloride
Acridine, 6-chloro-9-[[4-(diethylamino)-1-methylbutyl]amino]-2-methoxy-, dihydrochloride
1,4-Pentanediamine,N4-(6-chloro-2-methoxy-9-acridinyl)-N1,N1-diethyl-, hydrochloride (1:2)
2-Chloro-5-[[.omega.-(diethylamino)-.alpha.-methylbutyl)amino]-7-methoxyacridine dihydrochloride
Atebrin dihydrochloride, Mepacrine dihydrochloride, 6-Chloro-9-(4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamino)-2-methoxyacridine dihydrochloride
Quinacrine dihydrochloride,6-Chloro-9-(4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamino)-2-methoxyacridine dihydrochloride, Atebrin dihydrochloride, Mepacrine dihydrochloride | [EINECS(EC#)]
200-700-8 | [Molecular Formula]
C23H32Cl3N3O | [MDL Number]
MFCD00012659 | [MOL File]
69-05-6.mol | [Molecular Weight]
472.88 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
yellow crystals or powder | [Melting point ]
249-251℃ (Decomposition) | [density ]
1.2962 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.6300 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
+15C to +30C | [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Sonicated), Water (Slightly) | [form ]
Yellow solid | [pka]
pKa -6.3(H2O
t undefined
I not reported
but low) (Uncertain) | [color ]
Light Yellow to Yellow | [PH]
3.0~5.0 (20g/l, 25℃) | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | [biological source]
synthetic | [Water Solubility ]
Water: 33.33 mg/mL (70.48 mM) | [Merck ]
14,8044 | [BRN ]
4834013 | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Quinacrine hydrochloride (69-05-6) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
yellow crystals or powder | [Uses]
A non-specific PLA2 inhibitor. and acetylcholine receptor antagonist | [General Description]
Bright yellowish needles or bright yellow powder. Odorless. pH of a 1% aqueous solution is about 4.5.. Used as an anti-malarial drug. Moderately toxic. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Water soluble. | [Reactivity Profile]
QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE is an acidic salt of an amine. React as a weak acid to neutralize bases. | [Fire Hazard]
Flash point data for QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE are not available, but QUINACRINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE is probably combustible. | [Indications]
Quinacrine is no longer used extensively as an antimalarial
drug and has been largely replaced by the 4-
aminoquinolines. | [Brand name]
Dormison (Schering). | [Antimicrobial activity]
Mepacrine is active against the asexual erythrocytic stage of
all four Plasmodium spp. that infect humans and the gametocytes
of P. vivax and P. malariae. The enantiomers have equal
antimalarial activity. It exhibits broad activity
in experimental
models against T. cruzi, Leishmania spp., E. histolytica,
Trichomonas vaginalis, G. lamblia and Blastocystis hominis. It is
also active against tapeworms. | [Acquired resistance]
The structural resemblance to chloroquine suggests the likelihood
of cross-resistance with that drug, but evidence for this
is equivocal. | [Pharmaceutical Applications]
A synthetic acridine derivative, formulated as the hydrochloride
for oral use. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Target IC50: 4.4 μM in suppressing glibenclamide-sensitive K+-currents | [Pharmacokinetics]
Oral absorption: Good
Cmax 100 mg oral: 50 μg/L after 1–3 h
Plasma half-life: 5 days
Plasma protein binding: 85%
There is extensive tissue binding and a six-fold concentration into
leukocytes from plasma. About 10% of the daily dose is excreted
in the urine. It is widely distributed throughout the body. | [Clinical Use]
Giardiasis
Prophylaxis of malaria
Tapeworm infections | [Side effects]
Dizziness, headache and gastric problems are common.
Toxic psychoses, bone marrow depression, yellow skin and
exfoliative dermatitis are described. Poor toleration is noted,
especially
in children. It should not be used in combination
with 8-aminoquinolines. | [Synthesis]
Quinacrine, 6-chloro-9-(4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamino)-2-methoxy�acridine (37.1.4.3), is synthesized from 6,9-dichloro-2-methoxyacridine (37.1.4.2) and
aforementioned 4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamine (37.1.1.2). The 6,9-dichloro-
2-methoxyacridine (37.1.4.2) necessary for the synthesis is made in two stages. The initial
reaction of 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid and p-anizidine in the presence of copper dust and
potassium carbonate gives 2-(4-methoxyanilino)-4-chlorobenzoic acid (37.1.4.1), which
upon reaction with phosphorus oxychloride turns into the necessary 6,9-dichloro-
2-methoxyacridine (37.1.4.2).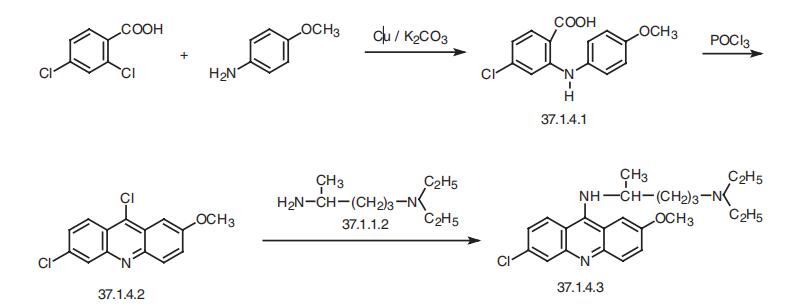
| [Purification Methods]
It crystallises from H2O (solubility is 2.8% at room temperature) as yellow crystals. It is slightly soluble in MeOH and EtOH. The free base crystallises from Me2CO or pet ether with m 86-88o, or aqueous EtOH with 85-87.5o. The bismethiodide has m 224o (from MeOH/EtOAc/Et3N), and the picrate has m 207-208o(dec) when crystallised from Me2CO/EtOH. It is an antimalarial, antiprotozoal and intercalates DNA. [Wolfe Antibiot 3 (Springer-Verlag) 203 1975, Beilstein 22 III/IV 6247, 22/12 V 235.] |
|
|