| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
2-CARBOXYETHYL ACRYLATE | [CAS]
24615-84-7 | [Synonyms]
B-CEA
sipomerb-cea
Einecs 246-359-9
RARECHEM AL BO 0311
B-Carboxyethyl acrylate
2-CARBOXYETHYL ACRYLATE
β-Carboxyethyl acrylate
hydracrylicacid,acrylate
beta-carboxyethylacrylate
2-carboxyethyl2-propenoate
.beta.-Carboxyethylacrylate
3-acryloyloxypropionic acid
3-(acryloyloxy)propanoic acid
3-prop-2-enoyloxypropanoicaci
2-CARBOXYETHYL ACRYLATE (Β-CEA)
beta-(acryloyloxy)propionicacid
2-carboxyethyl acrylate oligomers
2-Propenoicacid,2-carboxyethylester
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate oligomers, n=0-3
BETA-CARBOXYETHYL ACRYLATE ,2-Carboxyethyl acrylate
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate, 99%, stabilized with 1000 ppm MEHQ
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate contains 900-1100 ppM MEHQ as inhibitor
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate oligomers anhydrous, n=0-3, average MW~170 | [EINECS(EC#)]
246-359-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C6H8O4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00040709 | [MOL File]
24615-84-7.mol | [Molecular Weight]
144.13 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Boiling point ]
103 °C19 mm Hg(lit.)
| [density ]
1.214 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
| [refractive index ]
n20/D 1.457(lit.)
| [Fp ]
>230 °F
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C | [solubility ]
H2O: soluble
| [pka]
3.95±0.10(Predicted) | [PH]
2.95 (10wt. % in H2O) | [Water Solubility ]
H2O: soluble | [Merck ]
13,132 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C6H8O4/c1-2-6(9)10-4-3-5(7)8/h2H,1,3-4H2,(H,7,8) | [InChIKey]
CYUZOYPRAQASLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C(OCCC(O)=O)(=O)C=C | [LogP]
0.600 (est) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Hydracrylic acid acrylate (24615-84-7) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate is a highly versatile monomer extensively used to produce diverse polymers. It can be polymerized in solution or emulsion, producing vinyl-acrylic, acrylic, or styrenic-acrylic polymers with greater flexibility due to lower glass transition of itshomopolymer (<30C) and improved adhesion. It finds applications in various polymer production processes, including those geared towards optical applications like optical fibers, optical waveguides, and optical lenses. Moreover, 2-Carboxyethyl acrylate is instrumental in synthesizing polymers used in energy storage applications, such as fuel cells, batteries, and supercapacitors. 2-carboxyethyl acrylate could be used as a new monomer in the gel casting of alumina. This low-toxic, water-soluble monomer modifies the ceramic suspensions' rheological properties and minimizes the oxygen inhibition's negative effect [1-3].
| [Chemical Properties]
Colorless to light yellow viscid liquid | [Uses]
2-Carboxyethyl Acrylate is used in the preparation of DNase enzyme derivatives that act as potent preventative material of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation in biomaterials. | [Application]
2-Carboxyethyl acrylate can be polymerized in solution or emulsion to produce acrylic, vinyl acrylic, or styrene acrylic polymers, which are distinguished by their low glass transition temperatures (<30°C) as homopolymers. Greater elasticity, as well as improved adhesion. | [Preparation]
Synthesis of 1-ethoxyethyl acrylate (EEA) and protected 2-carboxyethyl acrylate (proCEA)
EEA and proCEA were synthesized following a previously published procedure and distilled prior to use. For the synthesis of proCEA (Figure 1), phosphoric acid (109 mg, 1.11 mmol) was weighed into a dry round bottom flask in a glovebox and then taken outside the glovebox, taking care that the phosphoric acid stayed dry. 2-Carboxyethyl acrylate (80 g, 555 mmol) and ethyl vinyl ether (48 g, 666 mmol) were added and the reaction was stirred for two days at room temperature. Hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O, ~1 g) was added, stirred for one hour and filtered off. Excess ethyl vinyl ether was removed under reduced pressure and the product was distilled under reduced pressure (80 °C, 1.3 mbar).
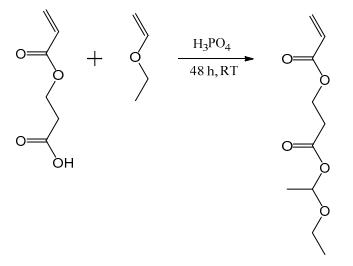
Figure 1 Synthesis of proCEA | [Hazard]
A severe skin irritant. | [References]
[1] Emilia Pietrzak, Mikolaj Szafran, Paulina Wiecinska. “2-carboxyethyl acrylate as a new monomer preventing negative effect of oxygen inhibition in gelcasting of alumina.” Ceramics International 42 12 (2016): Pages 13682-13688.
[2] Naveed Ullah . “Coupling of carboxymethyl starch with 2-carboxyethyl acrylate: A new sorbent for the wastewater remediation of methylene blue.” Environmental Research 219 (2023): Article 115091.
[3] Amit K. Tripathi, Donald C. Sundberg*, Jenna Vossoughi. “Partitioning of 2-Carboxyethyl Acrylate between Water and Vinyl Monomer Phases Applied to Emulsion Polymerization: Comparisons with Hydroxy Acrylate and Other Vinyl Acid Functional Monomers.” Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research 54 9 (2015): 2447–2452.
|
|
|