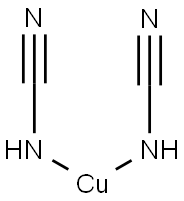
| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Cupric cyanide | [CAS]
14763-77-0 | [Synonyms]
Cupric cyanide
Copper(Ⅱ)cyanide
copper dicyanide
Cupric cyanide ISO 9001:2015 REACH | [EINECS(EC#)]
238-826-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C2CuN2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD01745912 | [MOL File]
14763-77-0.mol | [Molecular Weight]
115.581 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Cupric cyanide is a yellowish-green powder which decomposes on heating. | [Melting point ]
decomposes [CRC10] | [Boiling point ]
41°C (estimate) | [solubility ]
insoluble in H2O; soluble in acid solutions, alkaline solutions | [form ]
green powder | [color ]
green | [Water Solubility ]
insoluble H2O; soluble acids and alkalies [HAW93] | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Copper cyanide (Cu(CN)2) (14763-77-0) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
Cupric cyanide is a yellowish-green powder which decomposes on heating. | [Hazard]
Toxic. | [Potential Exposure]
Copper cyanide is used in electroplating copper on iron; and as an insecticide and a catalyst. | [First aid]
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 16 minutes, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated郘? | [Incompatibilities]
Contact with heat, strong acids (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3) forms deadly hydrogen cyanide gas. May release hydrogen cyanide on contact with moisture. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, acetylene gas, and chemically active metals, such as potassium, sodium, magnesium, and zinc. | [Description]
Cuprous cyanide is a white crystalline substance. Cupric cyanide, Cu(CN)2 is a yellowish-green powder which decomposes on heating. Molecularweight =89.56 (cuprous); 115.55 (cupric); Freezing/Melting point =473℃ (in nitrogen) (cuprous cyanide).Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 3, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Insolublein water. | [Waste Disposal]
Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill. Copper-containing wastes can be concentrated to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and reclaimed. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated by alkali; the cyanide destroyed by alkaline oxidation yielding a sludge which can be sent to a chemical waste landfill. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. | [storage]
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with coppercyanide you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Copper cyanide must be stored to avoid contactwith chemically active metals (such as potassium, sodium,magnesium, and zinc) since violent reactions occur. Storein tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from acetylene gas. | [Shipping]
Copper cyanide must carry a “POISONOUS/TOXIC MATERIALS” label. It is classified by DOT inHazard Class 6.1 and Packing Group II. |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [RIDADR ]
1587 | [HazardClass ]
6.1(a) | [PackingGroup ]
II | [Safety Profile]
Poison by
intraperitoneal route. See also CYANIDE
and COPPER COMPOUNDS.
Incompatible with magnesium. When heated
to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of
NOx and CN-. |
|
| Company Name: |
Camida
|
| Tel: |
+353-52-25455 |
| Website: |
www.camida.com |
|