| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 | [CAS]
104121-92-8 | [Synonyms]
ED-71
Eldecalcitol
El calciditol
Eldecalcitol(ED-71)
2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
1alpha,25-dihydroxy-2beta-(3-hydroxypropoxy)vitamin D3
2.beta.-(3-Hydroxypropoxy)-1.alpha.,25-dihydroxyvitaMin D3
Eldecalcitol {2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3}
(1R,Z)-5-((E)-2-((1R,7aR)-1-((R)-6-hydroxy-6-methylheptan-2-yl)-7a-methylhexahydro-1H-inden-4(2H)-ylidene)ethylidene)-2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-4-methylenecyclohexane-1,3-diol
1,3-Cyclohexanediol, 2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-4-methylene-5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-octahydro-1-[(1R)-5-hydroxy-1,5-dimethylhexyl]-7a-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-, (1R,2R,3R,5Z)-
(1S,2S,3S,5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(2R)-6-hydroxy-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-2-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-4-methylidenecyclohexane-1,3-diol | [EINECS(EC#)]
686-849-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C30H50O5 | [MDL Number]
MFCD25977156 | [MOL File]
104121-92-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
490.71 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
126-128℃ | [Boiling point ]
655.7±55.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.10 | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
Soluble in DMSO | [form ]
Powder | [pka]
13.80±0.60(Predicted) | [color ]
White to off-white | [InChIKey]
FZEXGDDBXLBRTD-AYIMTCTASA-N | [SMILES]
[C@@H]1(O)C/C(=C/C=C2\CCC[C@@]3(C)[C@@]\2([H])CC[C@@H]3[C@H](C)CCCC(O)(C)C)/C(=C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OCCCO |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Eldecalcitol (Edirol) was approved in January 2011 by the Japanese
Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare for the treatment of osteoporosis.
Because of vitamin D’s central role in the bone health, vitamin D and analogs of vitamin D have been used to treat patients diagnosed with osteoporosis.
Eldecalcitol is an analog of the active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, in which the lower cyclohexane ring contains a hydroxypropyl group. The synthesis of eldecalcitol involves the assembly of two units, a fully protected
(3S,4S,5R)-oct-1-en-7-yne-3,4,5-triol and a fused bicyclic system, (R)-6-
((1R,3aR,7aR,E)-4-(bromomethylene)-7a-methyloctahydro-1H-inden-1-
yl)-2-methylheptan-2-ol, through a Diels-Alder reaction to give fully
protected eldecalcitol. The hydroxyl groups are then deprotected to give
the parent molecule. Eldecalcitol binds to the vitaminDreceptor 2.7-fold
more potently than calcitriol, while only weakly inhibiting serum parathyroid hormone. | [Originator]
Chugai Pharmaceutical/Roche (Japan) | [Uses]
Eldecalcitol is a derivative of vitamin D3 (V676045) which is the vitamin that mediates intestinal calcium absorbtion, bone calcium metabolism and probably, muscle activity. | [Definition]
ChEBI: A hydroxycalciol that is calcitriol with a 3-hydroxypropoxy group at position 2. | [Brand name]
Edirol | [Clinical Use]
Eldecalcitol is a vitamin D3 analog approved in Japan for the
treatment of osteoporosis. Itwasdiscoveredby Chugai and co-developed
with Taisho. Eldecalcitol, a hormonally active calcitrol analog,
regulates calcium and bone metabolism. The drug was approved on
the basis of results from randomized, double-blinded, parallelgroup,
phase III studies taking place over three years that showed
eldecalcitol to significantly lower incidence of new vertebral fractures
compared to those receiving the comparator drug alfacalcidol. Discovery and SAR studies of vitamin D3 analogs leading
to the identification of eldecalcitol have been reported. In
addition, multiple syntheses, including parallel approaches, have
been reported in publications and patents. | [Synthesis]
The biomimetic vitamin D3 analog synthesis that was recently disclosed, based on an
earlier reported route for the commercial synthesis of alfacalcidol,
will be discussed here.
An Oppenauer oxidation converted commercially available cholesterol
141 to enone 142 in 80% yield. A second oxidation event
with DDQ provided dienone 143 in 75% yield. Treatment of 143
with sodium ethoxide in ethanol triggered migration of the enone
double bond into the B-ring, giving olefin 144 in 53% yield. Stereospecific
reduction of ketone 144 with sodium borohydride gave
alcohol 145 in 53% yield, which was then immediately protected
as the corresponding acetate with acetic anhydride to furnish
146. Next, further dehydrogenation of the B-ring was accomplished
using radical bromination of the olefin within 146 through
the use of NBS and catalytic AIBN, followed by elimination with
collidine. A subsequent saponification step ultimately gave rise to
the key diene 147. Next, in order to selectively epoxidize the A-ring
olefin, a unique ??protection?ˉ strategy was employed using phenyl-
1,2,4-triazole-3,5-dione (PTAD). Diels¨CAlder reaction between
diene 147 and PTAD produced cycloadduct 148 in 80% overall yield
from acetate 146. Protection of the alcohol as the corresponding
TBS ether preceeded a regio- and stereospecific epoxidation with
m-CPBA to afford 1,2a-epoxide 150 in 78% yield. Diels¨CAlder adduct
150 was then subjected to thermal conditions to affect a retro-[
4+2] reaction to give diene 151. Fluoride-mediated removal
of the TBS group prepared 3b-alcohol 152 in 95% yield. Subsequent
ring-opening reaction with 1,3-propane diol in the presence of
potassium t-butoxide, provided 3-hydroxy propoxy ether 153 in
29% yield. Microbial oxidation of intermediate 153 was accomplished
using an Amycolata autotrophica ATCC 33796 culture to obtain
eldecalcitol derivative 154 in 64% yield. Subjection of 154 to
400 watt light followed by thermolysis provided eldecalcitol (XII)
in 29% yield.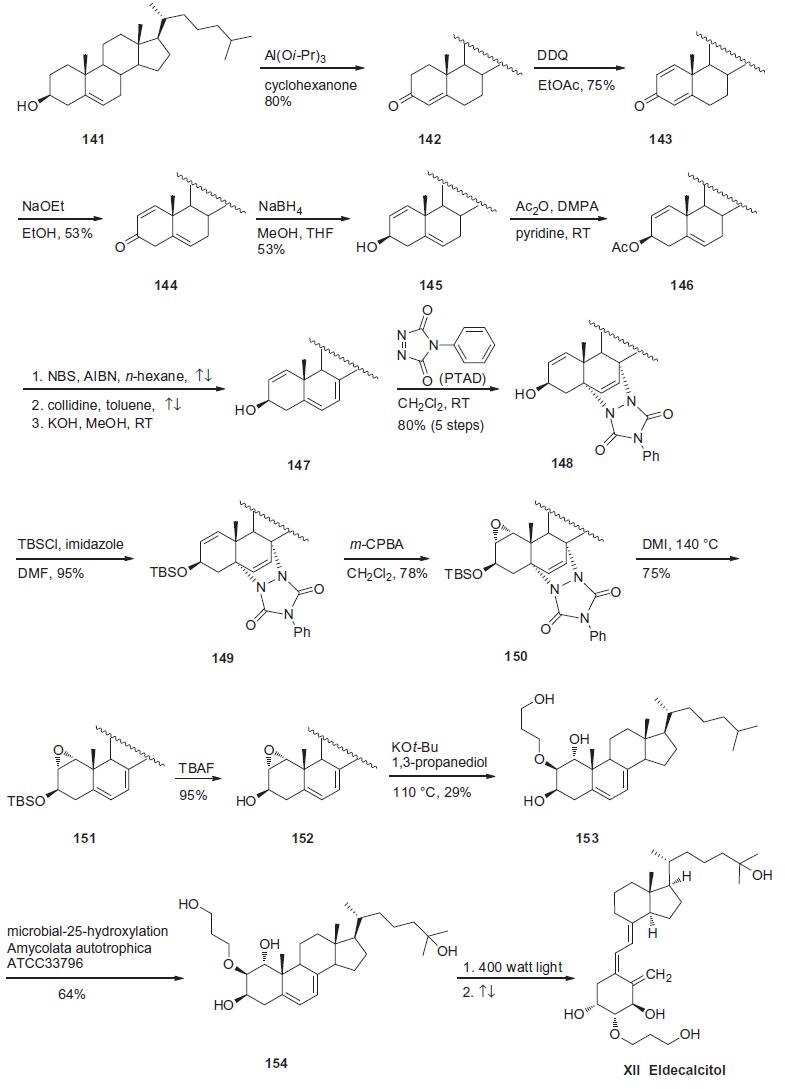
| [target]
osteoporosis |
|
|