| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Trastuzumab emtansine | [CAS]
1018448-65-1 | [Synonyms]
trastuzumab emtansine
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine
Ado-trastuzuMab-eMtansine cas nr
Ado-trastuzumab Emtansine (TDM-1) | [MDL Number]
MFCD28138412 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
T-DM1 is a human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER2)-targeted
antibody drug conjugate (ADC) that was approved in February 2013 by
the US FDA for use as a single agent for the treatment of patients with
HER2-positive, metastatic breast cancer (mBC) who previously received
treatment with trastuzumab and a taxane, separately, or in combination.
T-DM1 is composed of trastuzumab linked to the potent cytotoxic microtubule polymerization inhibitor DM1
(derivative of maytansine) via a stable uncleavable thioether linker. T-DM1
is produced by chemically crosslinking the cytotoxic maytansinoid derivative
to the lysine residues of trastuzumab such that there is an average of 3.5 cytotoxic molecules linked to each antibody. In addition to delivering DM1 to
tumor cells, T-DM1 retains the effector functions of trastuzumab, including
inhibition of HER2-mediated signal transduction and activation of antibodydependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. | [Originator]
Genentech, a member of the Roche Group (United States) | [Brand name]
Kadcyla | [Synthesis]
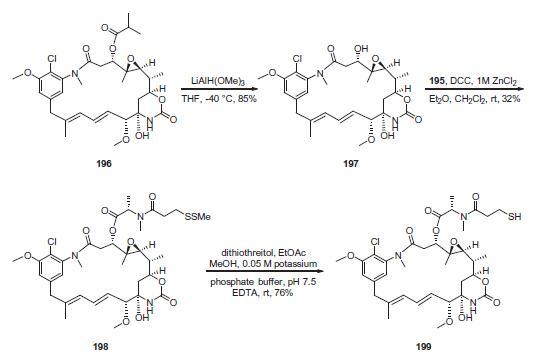
First, commercial 3-mercaptopropionic acid (191) was treated
with methanethiolsufonate to give the corresponding methyldithio
analog 192 in 90% yield. Activation of the acid with N-hydroxysuccinimide
in the presence of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-
carbodiimide (EDCI) provided the activated ester 193, which was
reacted with N-methyl-L-alanine (194) to give acid 195 in 60% yield
from compound 192.

Preparation of the DM1 linker-payload is described in
above. The starting material used for the production of DM1
is ansamitocin P-3 (196), which is produced via fermentation
of the microorganism Actinosynnema pretiosum. The ester group
of 196 was removed using a reductive process in the presence of
lithium trimethoxyaluminum hydride to give maytansinol 197 in
85% yield. The use of reductive conditions was required to
avoid subsequent elimination to the a,b-unsaturated amide.
Esterification with 195 in the presence of 1,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
(DCC) and zinc chloride provided DM1–SMe 198 in 32%
yield. Reductive removal of the dithiane using dithiothreitol
(DTT) in aqueous buffer at pH 7.5 gave DM1 thiol 199 in 76% yield,
which was utilized in the conjugation to trastuzumab (200).
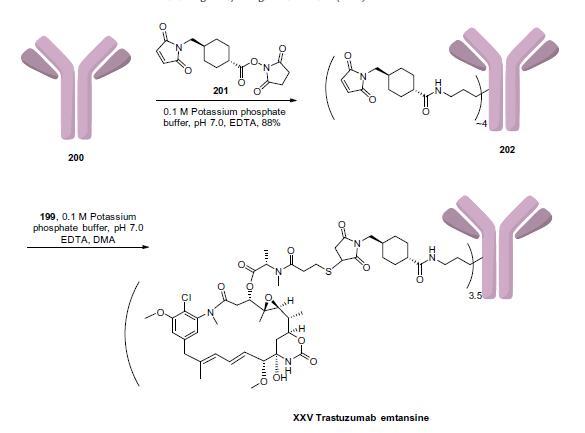
Completion of the synthesis of trastuzumab emtansine is
described in above. The surface accessible lysine residues of trastuzumab (200) were treated with succinimidyl-4-(N-maleimidomethyl)-
cyclohexane-carboxylate (SMCC, 201) in pH 7.0 buffer
to give amide 202 with approximately four SMCC molecules added
per antibody in 88% yield. Next, the free thiol group of
DM1 (199) was conjugated to the maleimide groups present on
202 to give trastuzumab emtansine (XXV) with an average 3.5
drug molecules loaded per antibody.
 | [storage]
Store at -20°C |
|
|










